|
|
IV.A.4. (XIV.F.) |
Relative enthalpies of isomers - Comparison of 298.15K enthalpies (kJ mol-1)
Isomers of H3OP
| index | Species | CAS number | Name | Relative experimental enthalpy (kJ mol-1) | sketch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | H3PO | 13840409 | Phosphine oxide | 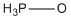 |
|
| b | H2POH | 25756870 | Phosphinous acid | 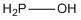 |
| semi-empirical | PM3 | -220.2 a -270.8 b |
|---|---|---|
| composite | G1 | NC NC |
| G2MP2 | NC NC |
|
| G2 | NC NC |
|
| G3 | NC NC |
|
| G3B3 | NC NC |
|
| G4 | NC NC |
|
| CBS-Q | NC NC |
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | cc-pV(T+d)Z | aug-cc-pV(T+d)Z | daug-cc-pVTZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hartree fock | HF | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | NC NC |
|
| density functional | LSDA | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||
| BLYP | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||
| B1B95 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||
| B3LYP | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||
| B3LYPultrafine | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||||
| B3PW91 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||
| mPW1PW91 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||
| M06-2X | NC | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||
| PBEPBE | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||
| PBEPBEultrafine | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||||
| PBE1PBE | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||
| HSEh1PBE | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||
| TPSSh | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||
| wB97X-D | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
||||||||||||||
| B97D3 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
||||||||||||||
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | cc-pV(T+d)Z | aug-cc-pV(T+d)Z | daug-cc-pVTZ | ||
| Moller Plesset perturbation | MP2 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||
| MP2=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||
| MP3 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||||||||||
| MP3=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||||||||||
| MP4 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||
| MP4=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||||||||
| Configuration interaction | CID | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||||
| CISD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||||||||||
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | cc-pV(T+d)Z | aug-cc-pV(T+d)Z | daug-cc-pVTZ | ||
| Quadratic configuration interaction | QCISD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||
| QCISD(T) | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||||
| Coupled Cluster | CCD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||
| CCSD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||
| CCSD=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | |||||||||||||
| CCSD(T) | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||
| CCSD(T)=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | ||||||||||||
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | cc-pV(T+d)Z | aug-cc-pV(T+d)Z | daug-cc-pVTZ |
| CEP-31G | CEP-31G* | CEP-121G | CEP-121G* | LANL2DZ | SDD | cc-pVTZ-PP | aug-cc-pVTZ-PP | Def2TZVPP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hartree fock | HF | -61960.4 a -62061.4 b |
-62331.3 a -62275.3 b |
-61990.7 a -62081.6 b |
-62344.4 a -62286.9 b |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
||
| density functional | B3LYP | -63403.5 a -63471.6 b |
-63680.4 a -63631.5 b |
-63431.4 a -63488.5 b |
-63699.5 a -63646.5 b |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
||
| PBEPBE | NC NC |
|||||||||
| Moller Plesset perturbation | MP2 | -62436.4 a -62512.6 b |
-63077.1 a -63020.4 b |
-62524.1 a -62584.1 b |
-63137.6 a -63075.4 b |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
For descriptions of the methods (AM1, HF, MP2, ...) and basis sets (3-21G, 3-21G*, 6-31G, ...) see the glossary in section I.C. Predefined means the basis set used is determined by the method.
gaw refers to the group additivity method implemeted in the NIST Chemistry Webbook.
See section III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.