Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3168 |
3057 |
7.40 |
61.94 |
0.67 |
0.81 |
| 2 |
A' |
3120 |
3010 |
22.44 |
71.14 |
0.70 |
0.82 |
| 3 |
A' |
3056 |
2949 |
3.62 |
98.42 |
0.00 |
0.01 |
| 4 |
A' |
3051 |
2944 |
15.95 |
89.84 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
| 5 |
A' |
3045 |
2939 |
15.48 |
114.37 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
| 6 |
A' |
1824 |
1760 |
222.76 |
3.40 |
0.30 |
0.46 |
| 7 |
A' |
1521 |
1467 |
5.29 |
1.00 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 8 |
A' |
1496 |
1444 |
1.86 |
19.30 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
A' |
1470 |
1418 |
11.67 |
13.33 |
0.71 |
0.83 |
| 10 |
A' |
1423 |
1374 |
4.87 |
4.18 |
0.71 |
0.83 |
| 11 |
A' |
1402 |
1353 |
27.16 |
1.20 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
A' |
1387 |
1338 |
23.11 |
3.49 |
0.60 |
0.75 |
| 13 |
A' |
1271 |
1226 |
401.62 |
0.38 |
0.22 |
0.36 |
| 14 |
A' |
1136 |
1097 |
15.25 |
6.28 |
0.12 |
0.22 |
| 15 |
A' |
1076 |
1038 |
103.63 |
2.42 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 16 |
A' |
1010 |
975 |
7.07 |
1.35 |
0.18 |
0.31 |
| 17 |
A' |
948 |
915 |
4.43 |
1.72 |
0.18 |
0.31 |
| 18 |
A' |
861 |
831 |
7.39 |
8.83 |
0.31 |
0.47 |
| 19 |
A' |
638 |
616 |
5.85 |
7.57 |
0.29 |
0.46 |
| 20 |
A' |
424 |
409 |
0.78 |
0.35 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
| 21 |
A' |
367 |
354 |
9.26 |
2.65 |
0.28 |
0.44 |
| 22 |
A' |
191 |
185 |
4.74 |
0.29 |
0.62 |
0.77 |
| 23 |
A" |
3125 |
3016 |
34.41 |
23.23 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 24 |
A" |
3121 |
3012 |
4.99 |
54.14 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 25 |
A" |
3088 |
2980 |
8.45 |
77.79 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 26 |
A" |
1486 |
1434 |
4.49 |
15.91 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 27 |
A" |
1476 |
1425 |
6.30 |
13.46 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 28 |
A" |
1291 |
1246 |
0.94 |
8.76 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 29 |
A" |
1183 |
1142 |
4.11 |
1.18 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 30 |
A" |
1065 |
1027 |
6.35 |
0.26 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 31 |
A" |
807 |
779 |
0.61 |
0.21 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 32 |
A" |
608 |
587 |
4.81 |
0.96 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 33 |
A" |
261 |
252 |
0.95 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 34 |
A" |
153 |
147 |
3.62 |
0.02 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 35 |
A" |
60 |
58 |
0.02 |
0.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 36 |
A" |
49 |
47 |
0.75 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25828.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.965) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24924.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
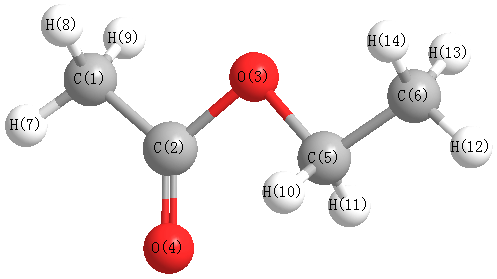
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.477 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.429 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.239 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.351 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.038 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.391 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.129 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.129 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.282 |
1.916 |
0.000 |
1.937 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
201.339 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.189 |