|
|
IV.A.4. (XIV.F.) |
Relative enthalpies of isomers - Comparison of 298.15K enthalpies (kJ mol-1)
Isomers of B2H4
| index | Species | CAS number | Name | Relative experimental enthalpy (kJ mol-1) | sketch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | HBHHBH | 9000348 | Diborane(4) C2V | 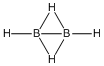 |
|
| b | B2H4 | 18099451 | Diborane(4) D2d | 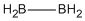 |
| semi-empirical | AM1 | 205.5 a |
|---|---|---|
| PM3 | 240.3 a | |
| PM6 | 376.4 a | |
| composite | G1 | NC NC |
| G2MP2 | NC NC |
|
| G2 | NC NC |
|
| G3 | NC NC |
|
| G3B3 | NC NC |
|
| G3MP2 | NC |
|
| G4 | NC NC |
|
| CBS-Q | NC NC |
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | daug-cc-pVDZ | daug-cc-pVTZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hartree fock | HF | NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
| density functional | LSDA | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
||
| BLYP | NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| B1B95 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
||||
| B3LYP | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|
| B3LYPultrafine | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||||||
| B3PW91 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| mPW1PW91 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| M06-2X | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
||||
| PBEPBE | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| PBEPBEultrafine | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||||||
| PBE1PBE | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| HSEh1PBE | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| TPSSh | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|
| wB97X-D | NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|
| B97D3 | NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
||
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | daug-cc-pVDZ | daug-cc-pVTZ | ||
| Moller Plesset perturbation | MP2 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
| MP2=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
|
| MP3 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||||||||||||
| MP3=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
||||
| MP4 | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
||||||||||
| MP4=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
||||||||||||
| B2PLYP | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| B2PLYP=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||
| Configuration interaction | CID | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
||||||||||
| CISD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
|||||||||||
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | daug-cc-pVDZ | daug-cc-pVTZ | ||
| Quadratic configuration interaction | QCISD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC | NC |
NC |
|||
| QCISD(T) | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||||||||||
| QCISD(T)=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
|||||||||||
| QCISD(TQ) | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC | NC NC |
|||||||||||||||
| QCISD(TQ)=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
||||||||||||||||
| Coupled Cluster | CCD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
||||
| CCSD | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
|||||||||||
| CCSD=FULL | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
||||||||||
| CCSD(T) | NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
NC |
|||||
| CCSD(T)=FULL | NC NC |
NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
|||||||||||
| STO-3G | 3-21G | 3-21G* | 6-31G | 6-31G* | 6-31G** | 6-31+G** | 6-311G* | 6-311G** | 6-31G(2df,p) | 6-311+G(3df,2p) | TZVP | cc-pVDZ | cc-pVTZ | cc-pVQZ | aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | daug-cc-pVDZ | daug-cc-pVTZ |
| CEP-31G | CEP-31G* | CEP-121G | CEP-121G* | LANL2DZ | SDD | cc-pVTZ-PP | aug-cc-pVTZ-PP | Def2TZVPP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hartree fock | HF | -19914.2 b |
-19852.3 a -19963.3 b |
-19937.0 b |
-19900.8 a -19992.1 b |
NC |
NC |
NC NC |
||
| density functional | LSDA | NC |
||||||||
| BLYP | NC |
|||||||||
| B1B95 | NC |
|||||||||
| B3LYP | -20575.7 a -20651.2 b |
-20629.3 a -20679.2 b |
-20613.3 a -20674.9 b |
-20672.4 a -20710.5 b |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
|||
| B3LYPultrafine | NC |
|||||||||
| B3PW91 | NC |
|||||||||
| mPW1PW91 | NC |
|||||||||
| M06-2X | NC |
|||||||||
| PBEPBE | NC NC |
|||||||||
| PBEPBEultrafine | NC |
|||||||||
| PBE1PBE | NC |
|||||||||
| HSEh1PBE | NC |
|||||||||
| TPSSh | NC |
|||||||||
| wB97X-D | -20592.4 a -20665.2 b |
-20647.4 a -20691.9 b |
-20633.7 a -20689.6 b |
-20692.9 a -20723.0 b |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC |
|||
| Moller Plesset perturbation | MP2 | -20065.5 a -20142.8 b |
-20260.0 a -20299.5 b |
-20139.5 a -20193.2 b |
-20335.8 a -20355.9 b |
NC NC |
NC NC |
NC NC |
||
| MP2=FULL | NC |
|||||||||
| MP3 | NC |
|||||||||
| MP3=FULL | NC |
|||||||||
| MP4 | NC |
|||||||||
| MP4=FULL | NC |
|||||||||
| B2PLYP | NC |
|||||||||
| B2PLYP=FULL | NC |
|||||||||
| Configuration interaction | CID | NC |
||||||||
| CISD | NC |
|||||||||
| Quadratic configuration interaction | QCISD | NC |
||||||||
| QCISD(T) | NC |
|||||||||
| QCISD(T)=FULL | NC |
|||||||||
| QCISD(TQ) | NC |
|||||||||
| Coupled Cluster | CCD | NC |
||||||||
| CCSD | NC |
|||||||||
| CCSD=FULL | NC |
|||||||||
| CCSD(T) | NC |
|||||||||
| CCSD(T)=FULL | NC |
For descriptions of the methods (AM1, HF, MP2, ...) and basis sets (3-21G, 3-21G*, 6-31G, ...) see the glossary in section I.C. Predefined means the basis set used is determined by the method.
gaw refers to the group additivity method implemeted in the NIST Chemistry Webbook.
See section III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.