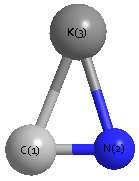Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.716489 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.715872 |
| HF Energy | -692.716489 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 61.252602 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.303 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.276 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.442 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.5789 | 3.7446 |
C2 | 2.5789 | | 1.1658 | N3 | 3.7446 | 1.1658 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.763 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.433 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.330 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.970 |
11.970 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.878 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.878 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.430 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.776 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.776 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-7.552 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -15.103 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.091 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.091 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.374 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
99.619 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.981 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.719076 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -692.719076 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.745376 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.204 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.393 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.218 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.5971 | 2.4223 |
C2 | 3.5971 | | 1.1747 | N3 | 2.4223 | 1.1747 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.769 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.222 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.547 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.926 |
11.926 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.772 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.772 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-32.785 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.007 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.007 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-10.014 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -20.028 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.047 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.047 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.234 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
88.602 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.413 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.722968 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.722826 |
| HF Energy | -692.722968 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 68.844083 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.039 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.624 |
-1.625 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.534 |
-1.428 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.7366 | 2.5245 |
C2 | 2.7366 | | 1.1746 | N3 | 2.5245 | 1.1746 | |
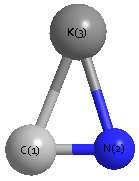 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
67.160 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
87.448 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.392 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.711 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.270 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.441 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.435 |
10.028 |
0.000 |
10.037 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.114 |
1.076 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.076 |
-26.300 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.011 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.459 |
1.076 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.076 |
-1.238 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.696 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.393 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.814 |
|---|
| xy | 1.076 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.394 |
-0.248 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.248 |
4.550 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.232 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
70.890 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.420 |