Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -209.157677 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -209.163576 |
| HF Energy | -209.157677 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 119.566126 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3650 |
3650 |
27.71 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3145 |
3145 |
15.73 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3055 |
3055 |
47.76 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3000 |
3000 |
79.65 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1862 |
1862 |
543.28 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1558 |
1558 |
28.62 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1514 |
1514 |
11.51 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1487 |
1487 |
6.48 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1419 |
1419 |
12.94 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1318 |
1318 |
121.34 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1189 |
1189 |
29.43 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1027 |
1027 |
49.96 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
625 |
625 |
15.66 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
356 |
356 |
8.50 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
3117 |
3117 |
25.87 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A" |
1509 |
1509 |
7.91 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
1155 |
1155 |
0.65 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
1063 |
1063 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A" |
619 |
619 |
145.41 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
184 |
184 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
20 |
20 |
0.96 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 16435.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 16435.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.289 |
-0.756 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
1.399 |
-1.224 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.571 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-1.335 |
1.126 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.624 |
-1.381 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.797 |
1.191 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-2.053 |
0.305 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
-1.517 |
1.733 |
0.889 |
| H9 |
-1.517 |
1.733 |
-0.889 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.2049 | 1.3577 | 2.4851 | 1.1065 | 2.0120 | 2.5708 | 3.2010 | 3.2010 |
O2 | 1.2049 | | 2.2757 | 3.6049 | 2.0290 | 2.4890 | 3.7754 | 4.2472 | 4.2472 | N3 | 1.3577 | 2.2757 | | 1.4456 | 2.0494 | 1.0097 | 2.0703 | 2.1077 | 2.1077 | C4 | 2.4851 | 3.6049 | 1.4456 | | 2.6057 | 2.1328 | 1.0907 | 1.0921 | 1.0921 | H5 | 1.1065 | 2.0290 | 2.0494 | 2.6057 | | 2.9386 | 2.2102 | 3.3598 | 3.3598 | H6 | 2.0120 | 2.4890 | 1.0097 | 2.1328 | 2.9386 | | 2.9846 | 2.5373 | 2.5373 | H7 | 2.5708 | 3.7754 | 2.0703 | 1.0907 | 2.2102 | 2.9846 | | 1.7660 | 1.7660 | H8 | 3.2010 | 4.2472 | 2.1077 | 1.0921 | 3.3598 | 2.5373 | 1.7660 | | 1.7780 | H9 | 3.2010 | 4.2472 | 2.1077 | 1.0921 | 3.3598 | 2.5373 | 1.7660 | 1.7780 | |
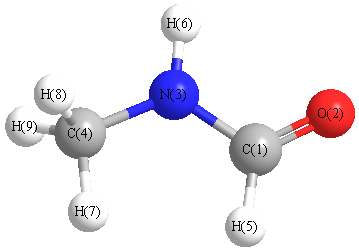 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
C4 |
124.844 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
115.612 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
125.151 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.706 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H5 |
112.143 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H7 |
108.619 |
| N3 |
C4 |
H8 |
111.553 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H9 |
111.553 |
| C4 |
N3 |
H6 |
119.544 |
|
H7 |
C4 |
H8 |
108.004 |
| H7 |
C4 |
H9 |
108.004 |
|
H8 |
C4 |
H9 |
108.980 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.247 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.392 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.572 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.511 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.356 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.232 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.240 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.240 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-3.065 |
2.731 |
0.000 |
4.105 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.403 |
4.072 |
0.000 |
| y |
4.072 |
-24.270 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.899 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.819 |
4.072 |
0.000 |
| y |
4.072 |
1.382 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.438 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.876 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.134 |
|---|
| xy | 4.072 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.531 |
-1.026 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.026 |
5.524 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.197 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
88.729 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.420 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -209.157677 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -209.163576 |
| HF Energy | -209.157677 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 119.566126 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -209.159844 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -209.165984 |
| HF Energy | -209.159844 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 121.821672 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3692 |
3692 |
29.18 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3188 |
3188 |
0.76 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3139 |
3139 |
28.13 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3077 |
3077 |
37.79 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3018 |
3018 |
106.46 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1845 |
1845 |
375.91 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1589 |
1589 |
131.89 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1530 |
1530 |
9.35 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1520 |
1520 |
38.11 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1467 |
1467 |
21.51 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1439 |
1439 |
3.50 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1244 |
1244 |
82.13 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1179 |
1179 |
20.43 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1167 |
1167 |
0.81 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1039 |
1039 |
0.50 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
988 |
988 |
24.74 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
786 |
786 |
1.47 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
561 |
561 |
61.22 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
317 |
317 |
13.34 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
283 |
283 |
82.61 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
85 |
85 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 16576.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 16576.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.863 |
0.433 |
0.003 |
| O2 |
1.355 |
-0.673 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.469 |
0.664 |
-0.020 |
| C4 |
-1.410 |
-0.441 |
0.005 |
| H5 |
1.468 |
1.353 |
0.018 |
| H6 |
-0.799 |
1.610 |
0.060 |
| H7 |
-2.409 |
-0.064 |
-0.208 |
| H8 |
-1.130 |
-1.171 |
-0.754 |
| H9 |
-1.409 |
-0.940 |
0.976 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.2103 | 1.3512 | 2.4346 | 1.1017 | 2.0376 | 3.3155 | 2.6677 | 2.8270 |
O2 | 1.2103 | | 2.2612 | 2.7748 | 2.0292 | 3.1398 | 3.8184 | 2.6447 | 2.9436 | N3 | 1.3512 | 2.2612 | | 1.4516 | 2.0558 | 1.0060 | 2.0807 | 2.0841 | 2.1095 | C4 | 2.4346 | 2.7748 | 1.4516 | | 3.3912 | 2.1412 | 1.0886 | 1.0896 | 1.0923 | H5 | 1.1017 | 2.0292 | 2.0558 | 3.3912 | | 2.2819 | 4.1336 | 3.7038 | 3.8017 | H6 | 2.0376 | 3.1398 | 1.0060 | 2.1412 | 2.2819 | | 2.3381 | 2.9172 | 2.7780 | H7 | 3.3155 | 3.8184 | 2.0807 | 1.0886 | 4.1336 | 2.3381 | | 1.7771 | 1.7804 | H8 | 2.6677 | 2.6447 | 2.0841 | 1.0896 | 3.7038 | 2.9172 | 1.7771 | | 1.7678 | H9 | 2.8270 | 2.9436 | 2.1095 | 1.0923 | 3.8017 | 2.7780 | 1.7804 | 1.7678 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
C4 |
120.558 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
118.899 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
123.856 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.656 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H5 |
113.487 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H7 |
109.156 |
| N3 |
C4 |
H8 |
109.363 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H9 |
111.258 |
| C4 |
N3 |
H6 |
120.116 |
|
H7 |
C4 |
H8 |
109.348 |
| H7 |
C4 |
H9 |
109.451 |
|
H8 |
C4 |
H9 |
108.238 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.240 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.397 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.579 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.529 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.355 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.235 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.267 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.235 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.850 |
2.662 |
0.000 |
3.900 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.473 |
2.717 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.717 |
-22.049 |
0.001 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.001 |
-24.928 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.984 |
2.717 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.717 |
3.152 |
0.001 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.001 |
-1.167 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.335 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.424 |
|---|
| xy | 2.717 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.870 |
-0.138 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.138 |
4.909 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.192 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
77.996 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.832 |
