Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -26.884221 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -26.887061 |
| HF Energy | -26.884221 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 10.350230 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
2750 |
2471 |
64.04 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
2175 |
1955 |
139.48 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1353 |
1216 |
53.57 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
894 |
803 |
13.01 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A2 |
906 |
814 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B1 |
2855 |
2565 |
135.84 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
B1 |
1142 |
1026 |
4.71 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
B2 |
1977 |
1777 |
9.85 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
B2 |
827 |
743 |
1.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7439.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6684.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| B1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.133 |
| H2 |
0.000 |
0.582 |
-1.002 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
-0.582 |
-1.002 |
| H4 |
-1.055 |
0.000 |
0.670 |
| H5 |
1.055 |
0.000 |
0.670 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
B1 |
H2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
| B1 | | 1.2757 | 1.2757 | 1.1839 | 1.1839 |
H2 | 1.2757 | | 1.1645 | 2.0611 | 2.0611 | H3 | 1.2757 | 1.1645 | | 2.0611 | 2.0611 | H4 | 1.1839 | 2.0611 | 2.0611 | | 2.1102 | H5 | 1.1839 | 2.0611 | 2.0611 | 2.1102 | |
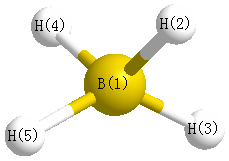 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| H2 |
B1 |
H3 |
54.310 |
|
H2 |
B1 |
H4 |
113.802 |
| H2 |
B1 |
H5 |
113.802 |
|
H3 |
B1 |
H4 |
113.802 |
| H3 |
B1 |
H5 |
113.802 |
|
H4 |
B1 |
H5 |
126.053 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
B |
-0.128 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.070 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.070 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.005 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.005 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.152 |
1.152 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-10.406 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-9.473 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-8.748 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.295 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.104 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.192 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.383 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.933 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.241 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.994 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.153 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
11.859 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
3.444 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -26.865975 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -26.865975 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 10.285599 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
2399 |
2156 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
1221 |
1097 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
B1 |
1261 |
1133 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
B2 |
2301 |
2068 |
5.69 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B2 |
995 |
894 |
14.83 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
E |
2429 |
2183 |
12.03 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
E |
2429 |
2183 |
12.03 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
E |
1005i |
903i |
579.50 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
E |
1005i |
903i |
579.50 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5512.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4953.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is D2d
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| B1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| H2 |
0.000 |
1.143 |
0.430 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
-1.143 |
0.430 |
| H4 |
-1.143 |
0.000 |
-0.430 |
| H5 |
1.143 |
0.000 |
-0.430 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
B1 |
H2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
| B1 | | 1.2212 | 1.2212 | 1.2212 | 1.2212 |
H2 | 1.2212 | | 2.2862 | 1.8308 | 1.8308 | H3 | 1.2212 | 2.2862 | | 1.8308 | 1.8308 | H4 | 1.2212 | 1.8308 | 1.8308 | | 2.2862 | H5 | 1.2212 | 1.8308 | 1.8308 | 2.2862 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| H2 |
B1 |
H3 |
138.800 |
|
H2 |
B1 |
H4 |
97.111 |
| H2 |
B1 |
H5 |
97.111 |
|
H3 |
B1 |
H4 |
97.111 |
| H3 |
B1 |
H5 |
97.111 |
|
H4 |
B1 |
H5 |
138.800 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
B |
-0.282 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.070 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.070 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.070 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.070 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-9.486 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-9.486 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.161 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.162 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.162 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.325 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.649 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.647 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.647 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.027 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
11.822 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
3.438 |
