Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -490.391508 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -490.392112 |
| HF Energy | -490.391508 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 80.212776 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3993 |
3587 |
528.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
2250 |
2022 |
1083.46 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
888 |
798 |
31.53 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
550 |
495 |
72.87 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
340 |
306 |
561.14 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
529 |
475 |
0.97 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4275.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3841.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
-0.098 |
1.673 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.506 |
0.000 |
| S3 |
0.015 |
-1.078 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.445 |
2.501 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.1714 | 2.7536 | 0.9897 |
C2 | 1.1714 | | 1.5840 | 2.0437 | S3 | 2.7536 | 1.5840 | | 3.6043 | H4 | 0.9897 | 2.0437 | 3.6043 | |
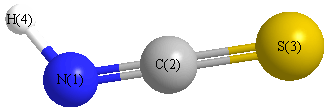 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
175.731 |
|
C2 |
N1 |
H4 |
141.899 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.693 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.384 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
-0.132 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.441 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.169 |
2.890 |
0.000 |
3.117 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.940 |
3.038 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.038 |
-18.627 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-25.598 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.828 |
3.038 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.038 |
6.642 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.815 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.629 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -6.313 |
|---|
| xy | 3.038 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.366 |
-0.151 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.151 |
8.387 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.267 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
60.650 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.788 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -490.390936 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -490.390936 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 80.127379 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σ |
4119 |
3701 |
895.48 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σ |
2355 |
2116 |
975.30 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σ |
852 |
766 |
81.17 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Π |
523 |
470 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Π |
523 |
470 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Π |
209i |
188i |
219.81 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Π |
209i |
188i |
219.81 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3977.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3573.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.665 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.512 |
| S3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.086 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.648 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.1535 | 2.7513 | 0.9824 |
C2 | 1.1535 | | 1.5979 | 2.1359 | S3 | 2.7513 | 1.5979 | | 3.7338 | H4 | 0.9824 | 2.1359 | 3.7338 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
180.000 |
|
C2 |
N1 |
H4 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.678 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.408 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
-0.172 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.443 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.001 |
4.001 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.584 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-25.584 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-16.019 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.783 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.783 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.565 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 19.131 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.265 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.265 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.076 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
60.855 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.801 |
