Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -663.467285 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -663.467285 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 157.497416 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2029 |
1823 |
278.29 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1030 |
925 |
110.37 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
865 |
777 |
190.16 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
759 |
682 |
7.60 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
312 |
280 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
360 |
323 |
3.23 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2676.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2405.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Cl1 |
-1.210 |
-0.279 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.884 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.288 |
0.450 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
1.444 |
-0.684 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Cl1 |
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
| Cl1 | | 1.6783 | 2.6016 | 2.6839 |
O2 | 1.6783 | | 1.3589 | 2.1312 | N3 | 2.6016 | 1.3589 | | 1.1443 | O4 | 2.6839 | 2.1312 | 1.1443 | |
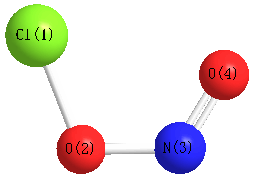 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Cl1 |
O2 |
N3 |
117.482 |
|
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
116.470 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
0.258 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.469 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
0.477 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.266 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.367 |
-0.307 |
0.000 |
0.478 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.651 |
1.775 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.775 |
-29.512 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-27.521 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.865 |
1.775 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.775 |
-1.926 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.061 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.122 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.861 |
|---|
| xy | 1.775 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.154 |
0.336 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.336 |
3.277 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.861 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
83.525 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.139 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -663.463531 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -663.463531 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 152.333207 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2065 |
1856 |
260.50 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1035 |
930 |
132.68 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
938 |
843 |
417.56 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
587 |
528 |
13.07 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
349 |
314 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
181 |
163 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2578.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2316.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Cl1 |
-1.417 |
-0.308 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.567 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.096 |
-0.286 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
2.053 |
0.338 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Cl1 |
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
| Cl1 | | 1.6655 | 2.5131 | 3.5297 |
O2 | 1.6655 | | 1.3886 | 2.0657 | N3 | 2.5131 | 1.3886 | | 1.1424 | O4 | 3.5297 | 2.0657 | 1.1424 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Cl1 |
O2 |
N3 |
110.416 |
|
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
109.010 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
0.273 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.474 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
0.439 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.237 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.741 |
-0.824 |
0.000 |
1.108 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.967 |
0.521 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.521 |
-29.219 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-27.537 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.411 |
0.521 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.521 |
-1.467 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.056 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.112 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.252 |
|---|
| xy | 0.521 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.151 |
0.866 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.866 |
2.500 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.875 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
99.562 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.978 |
