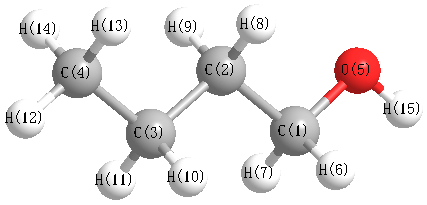
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
4116 |
3698 |
42.98 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3263 |
2932 |
61.29 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3209 |
2884 |
47.47 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3199 |
2874 |
23.02 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3187 |
2863 |
66.27 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3167 |
2845 |
42.02 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1683 |
1513 |
3.99 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1656 |
1488 |
3.15 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1644 |
1477 |
1.82 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1637 |
1471 |
0.34 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1617 |
1453 |
11.09 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1568 |
1409 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1539 |
1383 |
3.81 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1444 |
1297 |
26.56 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1357 |
1219 |
79.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1213 |
1090 |
4.41 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1188 |
1067 |
88.18 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1133 |
1018 |
1.67 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1073 |
964 |
1.37 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
975 |
876 |
11.66 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
472 |
424 |
14.23 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
421 |
379 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
201 |
181 |
2.89 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
3264 |
2933 |
136.02 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
3249 |
2919 |
22.67 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
3208 |
2882 |
12.03 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
3191 |
2867 |
56.05 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1644 |
1477 |
5.11 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1447 |
1301 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1443 |
1296 |
0.63 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
1370 |
1231 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
1305 |
1172 |
3.73 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
1036 |
931 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
880 |
791 |
1.82 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
798 |
717 |
0.69 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
303 |
273 |
144.45 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
265 |
238 |
0.97 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
128 |
115 |
2.28 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
117 |
105 |
5.36 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 32304.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29025.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.020 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.316 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.319 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.477 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.743 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.154 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.154 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.438 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.291 |
-1.670 |
0.000 |
1.695 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.450 |
-3.791 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.791 |
-35.160 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.209 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.734 |
-3.791 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.791 |
-3.831 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.904 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.808 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.710 |
|---|
| xy | -3.791 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.633 |
0.069 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.069 |
6.265 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.028 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
186.167 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.644 |