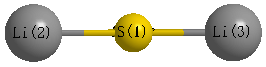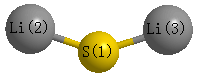Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/CEP-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -10.427540 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -10.427555 |
| HF Energy | -10.427540 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 3.130203 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/CEP-31G
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| Li2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.113 |
| Li3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.113 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
Li2 |
Li3 |
| S1 | | 2.1132 | 2.1132 |
Li2 | 2.1132 | | 4.2264 | Li3 | 2.1132 | 4.2264 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li2 |
S1 |
Li3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/CEP-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
-0.664 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Li |
0.332 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Li |
0.332 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.817 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.817 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
16.022 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.419 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-19.419 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
38.839 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 77.678 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.157 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.157 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.558 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
15.096 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
3.885 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/CEP-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -10.427540 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -10.427843 |
| HF Energy | -10.427540 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 3.130189 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/CEP-31G
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.000 |
| Li2 |
0.000 |
2.113 |
0.000 |
| Li3 |
0.000 |
-2.113 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
Li2 |
Li3 |
| S1 | | 2.1132 | 2.1132 |
Li2 | 2.1132 | | 4.2264 | Li3 | 2.1132 | 4.2264 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li2 |
S1 |
Li3 |
179.992 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/CEP-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
-0.664 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Li |
0.332 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Li |
0.332 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.001 |
0.001 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.817 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
16.022 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.817 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.420 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
38.839 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.420 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -38.839 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -38.839 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.157 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
10.558 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.157 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
15.096 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
3.885 |