Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/CEP-121G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3919 |
3540 |
28.58 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3843 |
3472 |
27.54 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3804 |
3436 |
28.48 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3270 |
2954 |
58.96 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3259 |
2944 |
80.79 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3222 |
2911 |
26.74 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3193 |
2884 |
32.89 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3185 |
2878 |
51.41 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1921 |
1735 |
690.96 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1800 |
1626 |
179.05 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1667 |
1506 |
4.16 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1634 |
1476 |
2.19 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1625 |
1468 |
4.29 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1612 |
1457 |
19.90 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1554 |
1404 |
2.99 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1534 |
1385 |
312.49 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1487 |
1344 |
51.05 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1414 |
1277 |
6.77 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1290 |
1166 |
14.78 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1259 |
1137 |
4.54 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1229 |
1110 |
66.04 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1146 |
1035 |
14.61 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1046 |
945 |
3.90 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
957 |
865 |
2.77 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
879 |
794 |
23.17 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
862 |
779 |
81.56 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
664 |
600 |
54.53 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
630 |
569 |
154.14 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
598 |
540 |
63.46 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
532 |
481 |
64.60 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
431 |
389 |
88.59 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
381 |
344 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
285 |
257 |
2.39 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
211 |
191 |
2.64 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
117 |
106 |
9.26 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
65 |
59 |
1.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28260.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9034) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25530.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
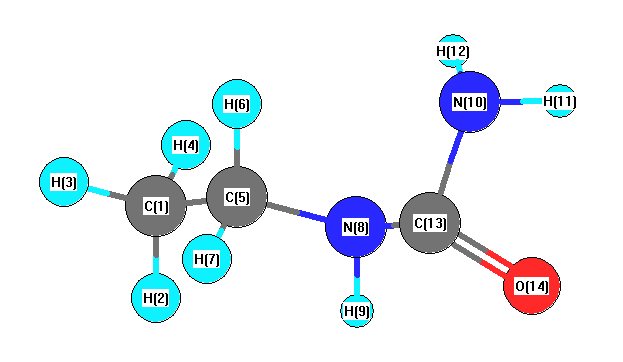
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/CEP-121G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.538 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.178 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.175 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.132 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.171 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
N |
-0.458 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.372 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
N |
-0.704 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.380 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.362 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
C |
0.361 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.470 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-3.264 |
2.992 |
-0.632 |
4.473 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.931 |
7.622 |
-2.132 |
| y |
7.622 |
-35.917 |
-2.134 |
| z |
-2.132 |
-2.134 |
-38.330 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.807 |
7.622 |
-2.132 |
| y |
7.622 |
2.713 |
-2.134 |
| z |
-2.132 |
-2.134 |
-0.906 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.812 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.014 |
|---|
| xy | 7.622 |
|---|
| xz | -2.132 |
|---|
| yz | -2.134 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.445 |
-0.285 |
0.102 |
| y |
-0.285 |
7.221 |
-0.056 |
| z |
0.102 |
-0.056 |
5.499 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
164.581 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.829 |