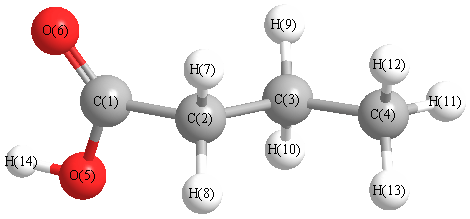Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
4111 |
3744 |
116.49 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3272 |
2979 |
36.19 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3237 |
2948 |
50.21 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3235 |
2945 |
55.38 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3212 |
2925 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3203 |
2917 |
19.55 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3179 |
2895 |
14.87 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3163 |
2880 |
36.45 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1980 |
1803 |
459.41 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1609 |
1465 |
7.49 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1594 |
1451 |
8.61 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1591 |
1449 |
1.15 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1587 |
1445 |
10.68 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1529 |
1392 |
17.29 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1510 |
1375 |
29.03 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1481 |
1349 |
47.01 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1422 |
1295 |
1.33 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1395 |
1270 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1365 |
1243 |
80.14 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1320 |
1202 |
125.47 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1201 |
1094 |
7.81 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1174 |
1069 |
75.56 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1114 |
1014 |
1.52 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
982 |
894 |
0.70 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
961 |
875 |
2.52 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
941 |
857 |
6.30 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
807 |
735 |
29.94 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
792 |
721 |
14.84 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
660 |
601 |
74.06 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
615 |
560 |
80.42 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
461 |
420 |
4.00 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
352 |
321 |
1.63 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
263 |
240 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
200 |
183 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
96 |
87 |
0.52 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
39 |
35 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27826.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9106) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25338.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
1.131 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.279 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.074 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.419 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.666 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.760 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
-0.110 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
-0.053 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.148 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
-0.135 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.072 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
-0.061 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
-0.059 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.161 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.440 |
1.536 |
0.370 |
2.138 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.674 |
5.632 |
0.243 |
| y |
5.632 |
-40.271 |
-1.622 |
| z |
0.243 |
-1.622 |
-36.421 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.672 |
5.632 |
0.243 |
| y |
5.632 |
-3.723 |
-1.622 |
| z |
0.243 |
-1.622 |
2.051 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.102 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.597 |
|---|
| xy | 5.632 |
|---|
| xz | 0.243 |
|---|
| yz | -1.622 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.246 |
-0.174 |
-0.258 |
| y |
-0.174 |
7.657 |
0.056 |
| z |
-0.258 |
0.056 |
6.860 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
207.689 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.411 |