Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -217.142611 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -217.150645 |
| HF Energy | -217.142611 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 128.353614 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3242 |
2952 |
49.52 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3205 |
2918 |
50.17 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3184 |
2899 |
21.54 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3164 |
2881 |
30.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1621 |
1476 |
2.41 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1611 |
1467 |
5.02 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1590 |
1448 |
1.27 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1548 |
1410 |
11.23 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1521 |
1385 |
3.38 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1435 |
1306 |
2.24 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1217 |
1108 |
1.68 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1143 |
1041 |
117.45 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1098 |
1000 |
36.12 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
958 |
873 |
7.41 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
478 |
436 |
7.77 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
292 |
265 |
4.37 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
3262 |
2970 |
93.40 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
3230 |
2942 |
28.22 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A" |
3210 |
2923 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
1594 |
1452 |
5.87 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
1413 |
1287 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
1365 |
1243 |
1.11 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
1283 |
1168 |
2.17 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
953 |
867 |
1.14 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
810 |
737 |
1.08 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
246 |
224 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
138 |
125 |
4.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22405.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9106) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20402.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.126 |
-0.785 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.724 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-1.461 |
1.173 |
0.000 |
| F4 |
1.459 |
-1.148 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.326 |
-1.227 |
0.887 |
| H6 |
-0.326 |
-1.227 |
-0.887 |
| H7 |
0.515 |
1.118 |
-0.878 |
| H8 |
0.515 |
1.118 |
0.878 |
| H9 |
-1.527 |
2.261 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
-1.989 |
0.808 |
-0.883 |
| H11 |
-1.989 |
0.808 |
0.883 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
F4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 1.5138 | 2.5205 | 1.3817 | 1.0895 | 1.0895 | 2.1308 | 2.1308 | 3.4657 | 2.7917 | 2.7917 |
C2 | 1.5138 | | 1.5283 | 2.3735 | 2.1676 | 2.1676 | 1.0911 | 1.0911 | 2.1670 | 2.1780 | 2.1780 | C3 | 2.5205 | 1.5283 | | 3.7304 | 2.7994 | 2.7994 | 2.1622 | 2.1622 | 1.0896 | 1.0917 | 1.0917 | F4 | 1.3817 | 2.3735 | 3.7304 | | 1.9951 | 1.9951 | 2.6070 | 2.6070 | 4.5323 | 4.0621 | 4.0621 | H5 | 1.0895 | 2.1676 | 2.7994 | 1.9951 | | 1.7741 | 3.0526 | 2.4907 | 3.7943 | 3.1689 | 2.6287 | H6 | 1.0895 | 2.1676 | 2.7994 | 1.9951 | 1.7741 | | 2.4907 | 3.0526 | 3.7943 | 2.6287 | 3.1689 | H7 | 2.1308 | 1.0911 | 2.1622 | 2.6070 | 3.0526 | 2.4907 | | 1.7557 | 2.4995 | 2.5229 | 3.0764 | H8 | 2.1308 | 1.0911 | 2.1622 | 2.6070 | 2.4907 | 3.0526 | 1.7557 | | 2.4995 | 3.0764 | 2.5229 | H9 | 3.4657 | 2.1670 | 1.0896 | 4.5323 | 3.7943 | 3.7943 | 2.4995 | 2.4995 | | 1.7613 | 1.7613 | H10 | 2.7917 | 2.1780 | 1.0917 | 4.0621 | 3.1689 | 2.6287 | 2.5229 | 3.0764 | 1.7613 | | 1.7654 | H11 | 2.7917 | 2.1780 | 1.0917 | 4.0621 | 2.6287 | 3.1689 | 3.0764 | 2.5229 | 1.7613 | 1.7654 | |
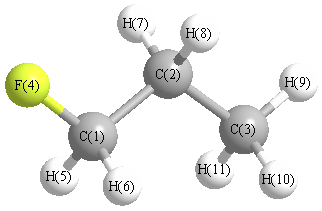 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.899 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.681 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.681 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F4 |
110.030 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.708 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.708 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.621 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
111.376 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.376 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
110.153 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.153 |
|
F4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.084 |
| F4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.084 |
|
H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.015 |
| H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
107.139 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
107.699 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.699 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.905 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
1.038 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.099 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.371 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.623 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.172 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.172 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
-0.065 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
-0.065 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.090 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
-0.062 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.062 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.977 |
0.859 |
0.000 |
2.156 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.192 |
2.553 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.553 |
-26.139 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.683 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.782 |
2.553 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.553 |
0.799 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.983 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 5.965 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.054 |
|---|
| xy | 2.553 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.945 |
-0.343 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.343 |
5.786 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.224 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
103.276 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.162 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -217.142688 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -217.142688 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 130.545232 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3262 |
2970 |
62.61 |
58.70 |
0.58 |
0.73 |
| 2 |
A |
3253 |
2962 |
43.26 |
35.92 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 3 |
A |
3233 |
2944 |
70.01 |
41.55 |
0.67 |
0.80 |
| 4 |
A |
3213 |
2926 |
38.20 |
115.16 |
0.10 |
0.19 |
| 5 |
A |
3202 |
2915 |
11.12 |
163.12 |
0.32 |
0.48 |
| 6 |
A |
3171 |
2887 |
14.38 |
205.83 |
0.04 |
0.08 |
| 7 |
A |
3165 |
2882 |
43.57 |
35.55 |
0.27 |
0.42 |
| 8 |
A |
1620 |
1475 |
1.32 |
2.15 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
A |
1602 |
1458 |
8.89 |
1.22 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 10 |
A |
1590 |
1448 |
5.91 |
6.08 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 11 |
A |
1578 |
1437 |
1.35 |
7.41 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 12 |
A |
1535 |
1398 |
11.95 |
0.94 |
0.08 |
0.14 |
| 13 |
A |
1528 |
1392 |
2.50 |
0.71 |
0.67 |
0.80 |
| 14 |
A |
1482 |
1349 |
1.28 |
0.70 |
0.61 |
0.76 |
| 15 |
A |
1398 |
1273 |
1.75 |
5.60 |
0.63 |
0.77 |
| 16 |
A |
1367 |
1245 |
2.19 |
2.44 |
0.73 |
0.85 |
| 17 |
A |
1267 |
1153 |
1.91 |
1.21 |
0.10 |
0.19 |
| 18 |
A |
1206 |
1098 |
18.74 |
2.13 |
0.64 |
0.78 |
| 19 |
A |
1163 |
1059 |
60.68 |
4.50 |
0.64 |
0.78 |
| 20 |
A |
1044 |
951 |
57.79 |
4.42 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 21 |
A |
982 |
894 |
4.51 |
0.50 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 22 |
A |
926 |
843 |
4.83 |
13.79 |
0.10 |
0.19 |
| 23 |
A |
820 |
747 |
1.35 |
0.82 |
0.21 |
0.35 |
| 24 |
A |
511 |
465 |
5.78 |
0.39 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 25 |
A |
337 |
307 |
1.42 |
0.31 |
0.21 |
0.34 |
| 26 |
A |
235 |
214 |
1.86 |
0.07 |
0.38 |
0.55 |
| 27 |
A |
149 |
136 |
2.91 |
0.12 |
0.71 |
0.83 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22418.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9106) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20414.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.800 |
0.504 |
0.300 |
| C2 |
-0.589 |
0.649 |
-0.284 |
| C3 |
-1.541 |
-0.476 |
0.118 |
| F4 |
1.400 |
-0.651 |
-0.172 |
| H5 |
1.442 |
1.335 |
0.014 |
| H6 |
0.776 |
0.427 |
1.387 |
| H7 |
-0.506 |
0.700 |
-1.371 |
| H8 |
-0.983 |
1.612 |
0.051 |
| H9 |
-2.525 |
-0.324 |
-0.327 |
| H10 |
-1.165 |
-1.443 |
-0.213 |
| H11 |
-1.667 |
-0.514 |
1.202 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
F4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 1.5137 | 2.5444 | 1.3840 | 1.0884 | 1.0896 | 2.1299 | 2.1139 | 3.4834 | 2.8131 | 2.8171 |
C2 | 1.5137 | | 1.5273 | 2.3786 | 2.1646 | 2.1684 | 1.0915 | 1.0933 | 2.1671 | 2.1705 | 2.1732 | C3 | 2.5444 | 1.5273 | | 2.9609 | 3.4914 | 2.7914 | 2.1614 | 2.1619 | 1.0903 | 1.0892 | 1.0920 | F4 | 1.3840 | 2.3786 | 2.9609 | | 1.9948 | 1.9948 | 2.6261 | 3.2937 | 3.9417 | 2.6851 | 3.3635 | H5 | 1.0884 | 2.1646 | 3.4914 | 1.9948 | | 1.7753 | 2.4734 | 2.4413 | 4.3136 | 3.8164 | 3.8074 | H6 | 1.0896 | 2.1684 | 2.7914 | 1.9948 | 1.7753 | | 3.0531 | 2.5060 | 3.7940 | 3.1337 | 2.6241 | H7 | 2.1299 | 1.0915 | 2.1614 | 2.6261 | 2.4734 | 3.0531 | | 1.7557 | 2.4930 | 2.5233 | 3.0730 | H8 | 2.1139 | 1.0933 | 2.1619 | 3.2937 | 2.4413 | 2.5060 | 1.7557 | | 2.5038 | 3.0714 | 2.5124 | H9 | 3.4834 | 2.1671 | 1.0903 | 3.9417 | 4.3136 | 3.7940 | 2.4930 | 2.5038 | | 1.7645 | 1.7638 | H10 | 2.8131 | 2.1705 | 1.0892 | 2.6851 | 3.8164 | 3.1337 | 2.5233 | 3.0714 | 1.7645 | | 1.7654 | H11 | 2.8171 | 2.1732 | 1.0920 | 3.3635 | 3.8074 | 2.6241 | 3.0730 | 2.5124 | 1.7638 | 1.7654 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
113.585 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.594 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
107.260 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F4 |
110.262 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.535 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.774 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.653 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
110.995 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.040 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
110.134 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.066 |
|
F4 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.958 |
| F4 |
C1 |
H6 |
106.894 |
|
H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.198 |
| H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.950 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.109 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.849 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
108.069 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
1.005 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.059 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.347 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.627 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.152 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.158 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
-0.106 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
-0.050 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.077 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
-0.044 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.080 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.102 |
1.628 |
0.545 |
2.040 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.463 |
2.011 |
0.811 |
| y |
2.011 |
-25.794 |
-0.045 |
| z |
0.811 |
-0.045 |
-24.903 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.114 |
2.011 |
0.811 |
| y |
2.011 |
0.389 |
-0.045 |
| z |
0.811 |
-0.045 |
1.725 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.450 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.669 |
|---|
| xy | 2.011 |
|---|
| xz | 0.811 |
|---|
| yz | -0.045 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.989 |
0.222 |
0.040 |
| y |
0.222 |
5.613 |
-0.027 |
| z |
0.040 |
-0.027 |
5.349 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
92.002 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.592 |
