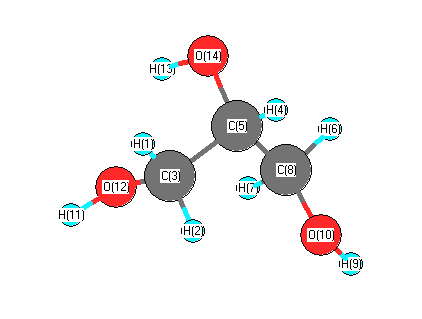
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
4193 |
3818 |
74.08 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
4190 |
3815 |
71.86 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
4145 |
3774 |
67.55 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3242 |
2952 |
37.69 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3235 |
2945 |
73.19 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3214 |
2927 |
22.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3180 |
2896 |
28.63 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3177 |
2893 |
73.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1628 |
1482 |
7.50 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1620 |
1476 |
9.97 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1584 |
1442 |
5.09 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1578 |
1437 |
5.66 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1532 |
1395 |
45.08 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1485 |
1352 |
8.86 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1417 |
1290 |
71.17 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1385 |
1262 |
14.10 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1347 |
1227 |
24.26 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1323 |
1205 |
11.96 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1281 |
1166 |
50.10 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1243 |
1132 |
24.59 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1216 |
1107 |
142.81 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1166 |
1061 |
112.17 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1148 |
1046 |
34.06 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1076 |
980 |
19.10 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1025 |
933 |
7.25 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
878 |
799 |
15.46 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
693 |
631 |
31.27 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
520 |
473 |
6.62 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
444 |
404 |
74.04 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
422 |
384 |
67.49 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
297 |
270 |
3.80 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
273 |
249 |
30.79 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
250 |
228 |
123.56 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
246 |
224 |
74.04 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
176 |
160 |
33.45 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
99 |
90 |
3.13 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27962.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9106) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25462.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
H |
-0.126 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
-0.114 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
1.112 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.206 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.277 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.070 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
-0.120 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
1.057 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
O |
-0.661 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.110 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
O |
-0.721 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.773 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.026 |
-1.906 |
-0.595 |
1.997 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
173.830 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.184 |