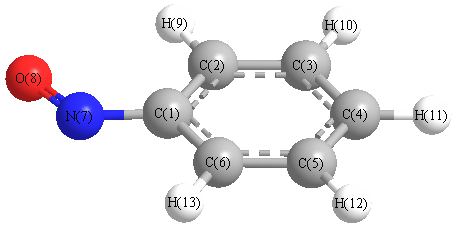
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3385 |
3083 |
2.74 |
85.30 |
0.16 |
0.28 |
| 2 |
A' |
3369 |
3068 |
8.71 |
181.87 |
0.11 |
0.20 |
| 3 |
A' |
3359 |
3058 |
12.70 |
51.12 |
0.32 |
0.48 |
| 4 |
A' |
3350 |
3050 |
7.92 |
96.65 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 5 |
A' |
3336 |
3038 |
0.37 |
43.22 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
A' |
1907 |
1736 |
203.85 |
102.81 |
0.32 |
0.49 |
| 7 |
A' |
1783 |
1624 |
2.45 |
45.51 |
0.53 |
0.70 |
| 8 |
A' |
1769 |
1611 |
51.95 |
101.90 |
0.55 |
0.71 |
| 9 |
A' |
1626 |
1481 |
0.51 |
5.92 |
0.44 |
0.61 |
| 10 |
A' |
1593 |
1451 |
16.20 |
2.54 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 11 |
A' |
1435 |
1307 |
6.81 |
1.12 |
0.39 |
0.56 |
| 12 |
A' |
1348 |
1227 |
15.36 |
0.98 |
0.57 |
0.72 |
| 13 |
A' |
1291 |
1176 |
38.13 |
41.46 |
0.23 |
0.38 |
| 14 |
A' |
1245 |
1133 |
54.10 |
41.74 |
0.15 |
0.26 |
| 15 |
A' |
1222 |
1112 |
22.24 |
12.64 |
0.73 |
0.85 |
| 16 |
A' |
1160 |
1056 |
1.05 |
0.90 |
0.69 |
0.82 |
| 17 |
A' |
1106 |
1007 |
2.06 |
14.14 |
0.03 |
0.07 |
| 18 |
A' |
1078 |
982 |
0.76 |
44.79 |
0.03 |
0.07 |
| 19 |
A' |
897 |
817 |
23.11 |
9.40 |
0.17 |
0.29 |
| 20 |
A' |
725 |
660 |
15.43 |
4.59 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 21 |
A' |
666 |
606 |
0.07 |
5.77 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 22 |
A' |
481 |
438 |
0.22 |
3.05 |
0.12 |
0.22 |
| 23 |
A' |
280 |
255 |
2.28 |
2.18 |
0.41 |
0.59 |
| 24 |
A" |
1096 |
998 |
0.00 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 25 |
A" |
1092 |
994 |
0.02 |
0.23 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 26 |
A" |
1047 |
954 |
5.21 |
0.12 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 27 |
A" |
939 |
855 |
0.03 |
1.26 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 28 |
A" |
839 |
764 |
77.81 |
2.06 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 29 |
A" |
734 |
669 |
24.43 |
0.08 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 30 |
A" |
516 |
470 |
4.36 |
0.31 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 31 |
A" |
455 |
415 |
0.01 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 32 |
A" |
273 |
249 |
0.04 |
1.58 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 33 |
A" |
111 |
102 |
0.21 |
0.11 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22756.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9106) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20721.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.669 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.463 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.546 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.403 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.680 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
0.332 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.281 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
O |
-0.610 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.438 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
-0.444 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.438 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
-0.423 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
-0.458 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.106 |
-3.312 |
0.000 |
3.492 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-42.061 |
2.544 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.544 |
-49.016 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-49.221 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
7.057 |
2.544 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.544 |
-3.375 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.682 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.364 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.955 |
|---|
| xy | 2.544 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
13.103 |
-1.426 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.426 |
15.027 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.102 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
247.465 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.731 |