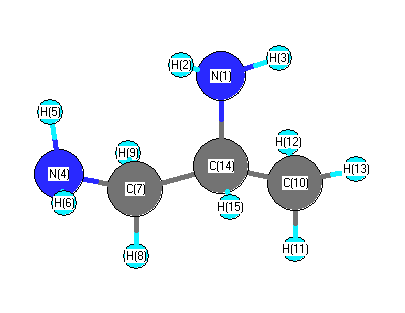
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3816 |
3474 |
2.61 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3807 |
3467 |
1.47 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3731 |
3398 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3723 |
3390 |
1.06 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3242 |
2952 |
67.52 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3226 |
2938 |
51.88 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3225 |
2936 |
17.90 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3180 |
2896 |
52.86 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3163 |
2880 |
22.98 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
3078 |
2802 |
81.48 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1783 |
1624 |
18.53 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1775 |
1616 |
52.38 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1599 |
1456 |
1.66 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1592 |
1450 |
6.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1588 |
1446 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1547 |
1408 |
0.36 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1521 |
1385 |
15.73 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1501 |
1367 |
8.76 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1480 |
1348 |
6.24 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1446 |
1317 |
9.62 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1354 |
1233 |
0.92 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1293 |
1178 |
4.53 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1257 |
1145 |
9.64 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1184 |
1078 |
25.31 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1122 |
1022 |
11.29 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1090 |
993 |
2.73 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1020 |
929 |
2.53 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
962 |
876 |
51.03 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
938 |
854 |
108.14 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
906 |
825 |
87.65 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
842 |
766 |
79.03 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
524 |
477 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
500 |
455 |
17.41 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
397 |
362 |
0.78 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
348 |
317 |
47.31 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
281 |
256 |
12.44 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
262 |
239 |
23.52 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
236 |
215 |
18.39 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
132 |
121 |
3.70 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 32334.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9106) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29443.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.273 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
-0.035 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.042 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.450 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.012 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.016 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
1.065 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
-0.116 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.089 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
C |
0.714 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.060 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.022 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
-0.097 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
-0.454 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
-0.157 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.034 |
0.928 |
1.713 |
2.206 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.790 |
-0.137 |
-0.049 |
| y |
-0.137 |
8.060 |
-0.012 |
| z |
-0.049 |
-0.012 |
7.319 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
144.172 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.007 |