Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
4196 |
3800 |
40.73 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3234 |
2929 |
69.95 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3231 |
2925 |
46.55 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3229 |
2924 |
92.17 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3218 |
2914 |
34.40 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3215 |
2912 |
2.38 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3165 |
2866 |
36.01 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3160 |
2862 |
15.81 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3154 |
2856 |
32.66 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
3128 |
2832 |
42.75 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1636 |
1482 |
7.13 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1630 |
1476 |
2.32 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1623 |
1469 |
4.09 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1613 |
1461 |
3.47 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1606 |
1455 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1558 |
1411 |
28.09 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1540 |
1394 |
1.72 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1530 |
1385 |
10.44 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1510 |
1368 |
12.73 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1484 |
1344 |
7.34 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1440 |
1304 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1348 |
1221 |
16.68 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1289 |
1167 |
0.67 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1244 |
1126 |
2.90 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1199 |
1086 |
65.18 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1187 |
1075 |
76.32 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1036 |
938 |
0.45 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
1015 |
919 |
6.29 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
996 |
902 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
970 |
878 |
5.51 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
862 |
780 |
5.04 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
522 |
472 |
5.50 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
445 |
403 |
0.75 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
380 |
344 |
5.24 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
311 |
281 |
88.57 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
280 |
253 |
5.80 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
254 |
230 |
36.96 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
231 |
210 |
3.80 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
129 |
117 |
4.10 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 31898.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9055) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28883.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
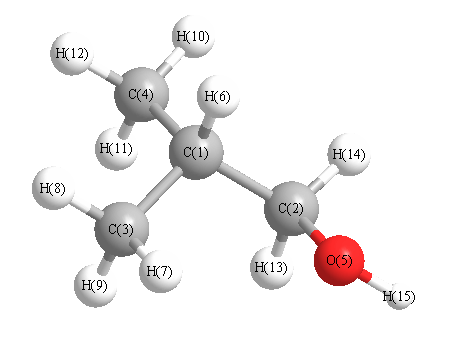
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.069 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.027 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.425 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.431 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.581 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.120 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.135 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.130 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.131 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.132 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.102 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.328 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.090 |
0.703 |
0.915 |
1.588 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.464 |
-2.380 |
-2.417 |
| y |
-2.380 |
-31.829 |
0.484 |
| z |
-2.417 |
0.484 |
-32.893 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.103 |
-2.380 |
-2.417 |
| y |
-2.380 |
2.849 |
0.484 |
| z |
-2.417 |
0.484 |
1.254 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.508 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.635 |
|---|
| xy | -2.380 |
|---|
| xz | -2.417 |
|---|
| yz | 0.484 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.172 |
-0.170 |
-0.022 |
| y |
-0.170 |
7.107 |
0.053 |
| z |
-0.022 |
0.053 |
6.279 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |