Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -130.432246 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -130.432246 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 35.648325 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3745 |
3402 |
23.33 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
1818 |
1652 |
43.39 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1491 |
1355 |
12.63 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
B1 |
452i |
411i |
261.45 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B2 |
3910 |
3553 |
24.79 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1394 |
1267 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5953.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9085) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5408.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-311G**
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.535 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.723 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.867 |
-1.022 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-0.867 |
-1.022 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
O2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.2581 | 0.9950 | 0.9950 |
O2 | 1.2581 | | 1.9492 | 1.9492 | H3 | 0.9950 | 1.9492 | | 1.7350 | H4 | 0.9950 | 1.9492 | 1.7350 | |
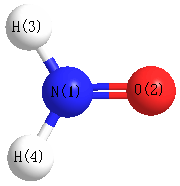 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O2 |
N1 |
H3 |
119.328 |
|
O2 |
N1 |
H4 |
119.328 |
| H3 |
N1 |
H4 |
121.344 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.183 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.263 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.223 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.223 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.833 |
2.833 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-12.314 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-9.699 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-10.856 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.036 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.886 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.151 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.301 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.615 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.028 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.367 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.772 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
16.626 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.077 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -130.432980 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -130.435507 |
| HF Energy | -130.432980 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 35.500239 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3711 |
3371 |
10.34 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1823 |
1657 |
37.22 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1442 |
1310 |
9.91 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
585 |
532 |
267.09 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
3854 |
3502 |
12.35 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
1432 |
1301 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6423.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9085) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5835.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
-0.031 |
0.544 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.031 |
-0.723 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.234 |
0.990 |
0.853 |
| H4 |
0.234 |
0.990 |
-0.853 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
O2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.2672 | 0.9982 | 0.9982 |
O2 | 1.2672 | | 1.9319 | 1.9319 | H3 | 0.9982 | 1.9319 | | 1.7058 | H4 | 0.9982 | 1.9319 | 1.7058 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O2 |
N1 |
H3 |
116.529 |
|
O2 |
N1 |
H4 |
116.529 |
| H3 |
N1 |
H4 |
117.390 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.182 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.253 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.218 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.218 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.910 |
2.589 |
0.000 |
2.744 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-12.112 |
0.859 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.859 |
-11.168 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.864 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.595 |
0.859 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.859 |
-0.180 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.776 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.551 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.943 |
|---|
| xy | 0.859 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.078 |
0.057 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.057 |
2.688 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.408 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
16.694 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.086 |
