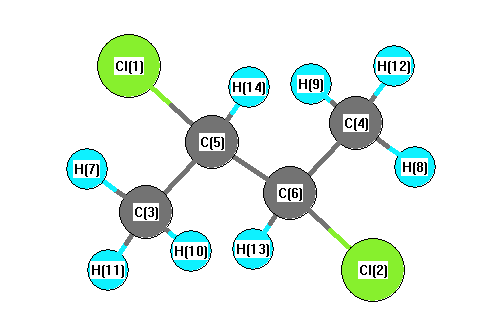
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
3276 |
2976 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
3270 |
2971 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
3255 |
2957 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
3190 |
2898 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Ag |
1615 |
1467 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Ag |
1610 |
1463 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Ag |
1549 |
1407 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
Ag |
1521 |
1382 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
Ag |
1404 |
1276 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
Ag |
1280 |
1163 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
Ag |
1221 |
1109 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
Ag |
1120 |
1018 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
Ag |
917 |
833 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Ag |
756 |
687 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
Ag |
507 |
461 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
Ag |
372 |
338 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
Ag |
304 |
276 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
Ag |
246 |
223 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
Au |
3286 |
2985 |
40.12 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
Au |
3276 |
2976 |
23.95 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
Au |
3255 |
2957 |
24.52 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
Au |
3189 |
2897 |
26.98 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
Au |
1615 |
1467 |
16.89 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
Au |
1607 |
1460 |
6.48 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
Au |
1546 |
1404 |
8.96 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
Au |
1433 |
1302 |
6.46 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
Au |
1345 |
1222 |
57.79 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
Au |
1181 |
1073 |
18.06 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
Au |
1103 |
1002 |
20.52 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
Au |
1041 |
946 |
20.93 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
Au |
697 |
633 |
132.26 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
Au |
389 |
354 |
4.56 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
Au |
357 |
324 |
2.86 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
Au |
263 |
239 |
3.13 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
Au |
217 |
197 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
Au |
65 |
59 |
4.47 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26638.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9085) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24201.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
-0.144 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Cl |
-0.144 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.180 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.180 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.209 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.209 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.131 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.131 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.109 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.109 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.169 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.169 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-51.509 |
2.566 |
-4.430 |
| y |
2.566 |
-54.660 |
4.300 |
| z |
-4.430 |
4.300 |
-56.482 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.062 |
2.566 |
-4.430 |
| y |
2.566 |
-0.665 |
4.300 |
| z |
-4.430 |
4.300 |
-3.398 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.795 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.151 |
|---|
| xy | 2.566 |
|---|
| xz | -4.430 |
|---|
| yz | 4.300 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.176 |
-0.465 |
0.698 |
| y |
-0.465 |
8.575 |
-2.349 |
| z |
0.698 |
-2.349 |
10.582 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
292.677 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
17.108 |