Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3852 |
3500 |
35.14 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3291 |
2990 |
21.20 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3235 |
2939 |
21.21 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3166 |
2876 |
6.21 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1938 |
1761 |
367.72 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1661 |
1509 |
33.67 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1621 |
1472 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1610 |
1463 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1577 |
1433 |
3.62 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1306 |
1187 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1266 |
1150 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1240 |
1127 |
7.20 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1000 |
908 |
1.95 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
563 |
511 |
67.63 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
449 |
408 |
64.63 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
241 |
219 |
4.44 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
209 |
190 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
121 |
110 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
3847 |
3495 |
10.96 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3291 |
2990 |
12.77 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3235 |
2939 |
81.52 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3165 |
2875 |
128.32 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1714 |
1557 |
470.54 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
1631 |
1482 |
2.14 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1609 |
1462 |
46.73 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1582 |
1437 |
6.76 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1372 |
1247 |
281.36 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1259 |
1144 |
23.50 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1243 |
1130 |
10.94 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1107 |
1005 |
4.13 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
866 |
786 |
51.21 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
791 |
719 |
20.43 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
529 |
481 |
119.80 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
347 |
315 |
45.81 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
133 |
121 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
129 |
117 |
9.76 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28097.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9085) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25526.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
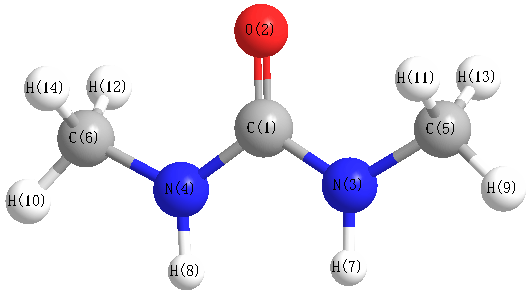
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.733 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.528 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.543 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.543 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.071 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.071 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.212 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.212 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.086 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.086 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.798 |
3.798 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-37.357 |
-1.990 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.990 |
-30.127 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-37.664 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.461 |
-1.990 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.990 |
7.384 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.922 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.845 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -7.230 |
|---|
| xy | -1.990 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.224 |
-0.329 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.329 |
8.367 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.899 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
190.344 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.797 |