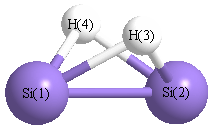Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -578.827612 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.827612 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 68.085830 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2494 |
2255 |
0.00 |
243.42 |
0.42 |
0.59 |
| 2 |
Σg |
832 |
752 |
0.00 |
188.72 |
0.09 |
0.17 |
| 3 |
Σu |
2490 |
2252 |
5.92 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 4 |
Πg |
560i |
506i |
0.00 |
115.55 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
Πg |
560i |
506i |
0.00 |
115.55 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
Πu |
518 |
468 |
0.57 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Πu |
518 |
468 |
0.57 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2865.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9042) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2591.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31+G**
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.971 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.971 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.422 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.422 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9424 | 1.4510 | 3.3933 |
Si2 | 1.9424 | | 3.3933 | 1.4510 | H3 | 1.4510 | 3.3933 | | 4.8443 | H4 | 3.3933 | 1.4510 | 4.8443 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.043 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.043 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.043 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.043 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.994 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-30.994 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.556 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.719 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.719 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.438 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 18.875 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.379 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
6.379 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
15.048 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
55.536 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.452 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -578.853944 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.853944 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.529495 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2350 |
2125 |
0.00 |
447.57 |
0.63 |
0.77 |
| 2 |
Ag |
664 |
601 |
0.00 |
77.23 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 3 |
Ag |
549 |
497 |
0.00 |
630.22 |
0.16 |
0.27 |
| 4 |
Au |
376i |
340i |
408.88 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Bu |
2351 |
2126 |
215.68 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
Bu |
29 |
26 |
146.08 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2783.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9042) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2517.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
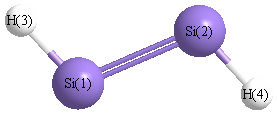
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.042 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.042 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.176 |
1.936 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.176 |
-1.936 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.0847 | 1.4769 | 3.2023 |
Si2 | 2.0847 | | 3.2023 | 1.4769 | H3 | 1.4769 | 3.2023 | | 4.5305 | H4 | 3.2023 | 1.4769 | 4.5305 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
127.253 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
127.253 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.095 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.095 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.336 |
-0.003 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.003 |
-23.127 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.908 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.818 |
-0.003 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.003 |
7.995 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-5.177 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -10.353 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -7.208 |
|---|
| xy | -0.003 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.363 |
-0.875 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.875 |
17.075 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.531 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
58.457 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.646 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -578.893313 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.893313 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.503457 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1718 |
1553 |
17.54 |
65.36 |
0.10 |
0.18 |
| 2 |
A1 |
1077 |
974 |
91.80 |
4.52 |
0.57 |
0.73 |
| 3 |
A1 |
599 |
542 |
0.24 |
99.04 |
0.31 |
0.48 |
| 4 |
A2 |
973 |
880 |
0.00 |
6.12 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B1 |
1629 |
1473 |
35.11 |
21.20 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
1171 |
1059 |
561.18 |
4.85 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3582.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9042) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3239.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.090 |
-0.053 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.090 |
-0.053 |
| H3 |
0.990 |
0.000 |
0.748 |
| H4 |
-0.990 |
0.000 |
0.748 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1807 | 1.6767 | 1.6767 |
Si2 | 2.1807 | | 1.6767 | 1.6767 | H3 | 1.6767 | 1.6767 | | 1.9799 | H4 | 1.6767 | 1.6767 | 1.9799 | |
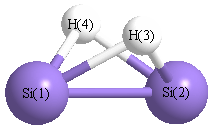 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
49.438 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.438 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.224 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.224 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.224 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.224 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.671 |
0.671 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.687 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-33.911 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-29.362 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.949 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-5.886 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.937 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.874 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 7.224 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.688 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.488 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.990 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
55.176 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.428 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -578.871476 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.871476 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.939387 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2385 |
2156 |
86.20 |
256.78 |
0.44 |
0.61 |
| 2 |
A' |
1773 |
1603 |
141.04 |
97.40 |
0.17 |
0.29 |
| 3 |
A' |
1020 |
923 |
139.96 |
10.70 |
0.62 |
0.77 |
| 4 |
A' |
666 |
603 |
36.97 |
151.38 |
0.16 |
0.28 |
| 5 |
A' |
430 |
389 |
22.68 |
2.46 |
0.02 |
0.04 |
| 6 |
A" |
143i |
129i |
98.45 |
65.87 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3065.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9042) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2771.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.056 |
-1.127 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.056 |
0.956 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.269 |
0.025 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.296 |
2.382 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.0830 | 1.7559 | 3.5273 |
Si2 | 2.0830 | | 1.6185 | 1.4695 | H3 | 1.7559 | 1.6185 | | 2.5495 | H4 | 3.5273 | 1.4695 | 2.5495 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
166.127 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.966 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.260 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.013 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.188 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.084 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.232 |
1.291 |
0.000 |
1.312 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.430 |
0.119 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.119 |
-27.209 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.969 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.158 |
0.119 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.119 |
2.491 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.649 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -9.298 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.222 |
|---|
| xy | 0.119 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.136 |
0.159 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.159 |
15.172 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.350 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.070 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.488 |