Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -168.855073 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -168.859237 |
| HF Energy | -168.855073 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.474688 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3987 |
3600 |
62.15 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3845 |
3471 |
57.62 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3266 |
2949 |
72.33 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1889 |
1706 |
473.45 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1818 |
1642 |
50.48 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1553 |
1402 |
30.17 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1400 |
1264 |
164.60 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1180 |
1065 |
7.21 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
619 |
559 |
19.14 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1180 |
1066 |
5.38 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
737 |
666 |
399.88 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
580 |
523 |
130.95 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11026.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9029) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9956.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.420 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
1.202 |
0.208 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.947 |
-0.541 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.395 |
1.427 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.675 |
-1.496 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
-1.913 |
-0.323 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.2201 | 1.3496 | 1.0813 | 2.0312 | 2.0523 |
O2 | 1.2201 | | 2.2758 | 2.0082 | 2.5345 | 3.1597 | N3 | 1.3496 | 2.2758 | | 2.0441 | 0.9929 | 0.9902 | H4 | 1.0813 | 2.0082 | 2.0441 | | 2.9361 | 2.3168 | H5 | 2.0312 | 2.5345 | 0.9929 | 2.9361 | | 1.7058 | H6 | 2.0523 | 3.1597 | 0.9902 | 2.3168 | 1.7058 | |
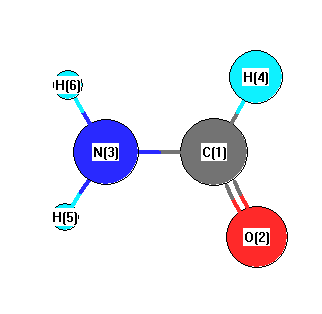 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
119.478 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
121.846 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
124.580 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
121.401 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
114.019 |
|
H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
118.676 |
Electronic energy levels
Electronic state
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.547 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.578 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.902 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.391 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.378 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-4.512 |
-0.302 |
0.000 |
4.522 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.422 |
-0.309 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.309 |
-14.441 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.788 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.808 |
-0.309 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.309 |
4.665 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.856 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.713 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.982 |
|---|
| xy | -0.309 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.838 |
0.160 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.160 |
2.638 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.120 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.898 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.395 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -168.855073 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -168.859237 |
| HF Energy | -168.855073 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.477123 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3987 |
3600 |
62.13 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3844 |
3471 |
57.62 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3264 |
2947 |
72.22 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1889 |
1706 |
473.59 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1819 |
1642 |
50.19 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1552 |
1402 |
30.18 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1400 |
1264 |
164.69 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1181 |
1066 |
5.38 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1180 |
1066 |
7.11 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
738 |
666 |
400.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
620 |
560 |
19.17 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
579 |
523 |
130.79 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11026.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9029) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9955.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.154 |
0.391 |
-0.000 |
| O2 |
1.194 |
-0.247 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.080 |
-0.157 |
-0.000 |
| H4 |
0.156 |
1.472 |
-0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.176 |
-1.145 |
-0.000 |
| H6 |
-1.898 |
0.400 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.2202 | 1.3495 | 1.0815 | 2.0314 | 2.0522 |
O2 | 1.2202 | | 2.2753 | 2.0084 | 2.5340 | 3.1593 | N3 | 1.3495 | 2.2753 | | 2.0446 | 0.9930 | 0.9901 | H4 | 1.0815 | 2.0084 | 2.0446 | | 2.9367 | 2.3175 | H5 | 2.0314 | 2.5340 | 0.9930 | 2.9367 | | 1.7056 | H6 | 2.0522 | 3.1593 | 0.9901 | 2.3175 | 1.7056 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
119.491 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
121.853 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
124.535 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
121.408 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
114.057 |
|
H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
118.655 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.547 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.578 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.902 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.391 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.377 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-4.309 |
1.374 |
0.001 |
4.522 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-18.963 |
1.476 |
-0.002 |
| y |
1.476 |
-14.898 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.002 |
0.001 |
-18.788 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.120 |
1.476 |
-0.002 |
| y |
1.476 |
3.978 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.002 |
0.001 |
-1.858 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.716 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.065 |
|---|
| xy | 1.476 |
|---|
| xz | -0.002 |
|---|
| yz | 0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.785 |
-0.293 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.293 |
2.691 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.120 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.892 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.395 |
