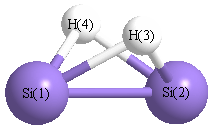Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.036362 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.826258 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 66.758882 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2388 |
2230 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
742 |
693 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
2386 |
2228 |
4.05 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
669i |
624i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
669i |
624i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
363 |
339 |
3.51 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
363 |
339 |
3.51 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2452.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9338) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2290.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.994 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.994 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.451 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.451 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9876 | 1.4572 | 3.4449 |
Si2 | 1.9876 | | 3.4449 | 1.4572 | H3 | 1.4572 | 3.4449 | | 4.9021 | H4 | 3.4449 | 1.4572 | 4.9021 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.073415 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.853405 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.718432 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2251 |
2102 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
636 |
594 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
573 |
536 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Au |
363 |
339 |
25.76 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Bu |
2256 |
2106 |
178.65 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Bu |
319 |
298 |
27.60 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3198.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9338) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2987.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
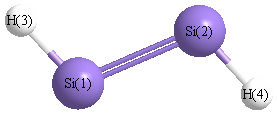
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.059 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.059 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.233 |
1.885 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.233 |
-1.885 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1180 | 1.4835 | 3.1913 |
Si2 | 2.1180 | | 3.1913 | 1.4835 | H3 | 1.4835 | 3.1913 | | 4.5038 | H4 | 3.1913 | 1.4835 | 4.5038 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
123.820 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
123.820 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.101531 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.892797 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.095720 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1722 |
1608 |
8.56 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
990 |
925 |
57.88 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
544 |
508 |
1.34 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A2 |
1165 |
1088 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1 |
1624 |
1516 |
19.56 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1262 |
1179 |
453.29 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3653.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9338) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3411.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.104 |
-0.051 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.104 |
-0.051 |
| H3 |
0.982 |
0.000 |
0.708 |
| H4 |
-0.982 |
0.000 |
0.708 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.2077 | 1.6605 | 1.6605 |
Si2 | 2.2077 | | 1.6605 | 1.6605 | H3 | 1.6605 | 1.6605 | | 1.9635 | H4 | 1.6605 | 1.6605 | 1.9635 | |
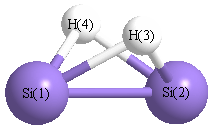 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
48.334 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.334 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.083302 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.870397 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.041779 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2252 |
2103 |
110.72 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1726 |
1612 |
101.42 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1166 |
1089 |
175.35 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
618 |
577 |
15.47 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
467 |
436 |
5.74 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
83i |
77i |
50.47 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3072.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9338) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2869.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.061 |
-1.145 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.061 |
0.978 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.225 |
-0.018 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.495 |
2.351 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1232 | 1.7104 | 3.5403 |
Si2 | 2.1232 | | 1.6268 | 1.4814 | H3 | 1.7104 | 1.6268 | | 2.4791 | H4 | 3.5403 | 1.4814 | 2.4791 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
157.956 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.770 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability