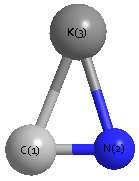Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.124429 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.123820 |
| HF Energy | -691.510372 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 60.556692 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.319 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.294 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.470 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.6129 | 3.7890 |
C2 | 2.6129 | | 1.1762 | N3 | 3.7890 | 1.1762 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.126853 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -691.517798 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.045492 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.219 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.419 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.235 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.6375 | 2.4544 |
C2 | 3.6375 | | 1.1831 | N3 | 2.4544 | 1.1831 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.130998 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.130857 |
| HF Energy | -691.518416 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 68.222200 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.049 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.630 |
-1.627 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.540 |
-1.453 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.7489 | 2.5596 |
C2 | 2.7489 | | 1.1832 | N3 | 2.5596 | 1.1832 | |
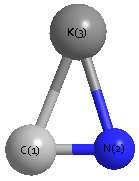 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
68.305 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
86.258 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.437 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability