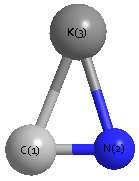Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -691.782898 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -691.782396 |
| HF Energy | -691.450941 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 59.762240 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/6-31+G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.338 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.315 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.504 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.6531 | 3.8413 |
C2 | 2.6531 | | 1.1882 | N3 | 3.8413 | 1.1882 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -691.785984 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -691.785355 |
| HF Energy | -691.459169 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.040519 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/6-31+G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.241 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.457 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.262 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.6973 | 2.5023 |
C2 | 3.6973 | | 1.1950 | N3 | 2.5023 | 1.1950 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -691.788012 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -691.787865 |
| HF Energy | -691.457361 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 67.290114 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.065 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.637 |
-1.645 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.546 |
-1.481 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.7845 | 2.6042 |
C2 | 2.7845 | | 1.1947 | N3 | 2.6042 | 1.1947 | |
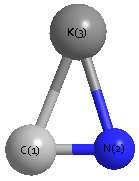 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
68.866 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
85.799 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.335 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability