Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3105 |
3080 |
3.16 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3105 |
3080 |
2.98 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3072 |
3047 |
13.28 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3051 |
3026 |
5.82 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3038 |
3013 |
16.39 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3006 |
2981 |
1.64 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3000 |
2975 |
6.88 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2984 |
2960 |
18.87 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1496 |
1484 |
6.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1488 |
1476 |
7.67 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1454 |
1442 |
7.65 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1450 |
1438 |
4.40 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1445 |
1433 |
2.43 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1400 |
1389 |
1.80 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1322 |
1311 |
7.17 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1282 |
1272 |
28.96 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1250 |
1240 |
52.16 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1234 |
1224 |
91.37 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1080 |
1071 |
100.10 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1049 |
1040 |
2.18 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1022 |
1013 |
38.31 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
960 |
952 |
3.89 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
945 |
937 |
16.46 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
939 |
931 |
9.10 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
774 |
768 |
30.92 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
669 |
663 |
50.73 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
578 |
573 |
14.58 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
460 |
457 |
13.57 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
406 |
403 |
19.00 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
366 |
363 |
7.44 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
290 |
288 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
266 |
263 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
213 |
211 |
1.68 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
194 |
193 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
184 |
182 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
83 |
82 |
2.19 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24328.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9919) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24130.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
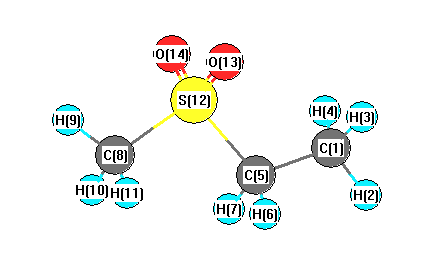
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.420 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.180 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.411 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.582 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.181 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
S |
0.999 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
O |
-0.498 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.495 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.924 |
2.750 |
-2.049 |
4.507 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-43.829 |
-4.966 |
-1.235 |
| y |
-4.966 |
-41.948 |
-0.541 |
| z |
-1.235 |
-0.541 |
-47.814 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.052 |
-4.966 |
-1.235 |
| y |
-4.966 |
3.873 |
-0.541 |
| z |
-1.235 |
-0.541 |
-4.925 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -9.850 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.881 |
|---|
| xy | -4.966 |
|---|
| xz | -1.235 |
|---|
| yz | -0.541 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.366 |
-0.237 |
0.049 |
| y |
-0.237 |
8.224 |
0.032 |
| z |
0.049 |
0.032 |
7.817 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
198.886 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.103 |