Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3084 |
3067 |
5.54 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3059 |
3043 |
15.86 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3035 |
3018 |
22.12 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3021 |
3004 |
14.68 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3010 |
2994 |
4.51 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2998 |
2982 |
2.62 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2968 |
2951 |
24.97 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2961 |
2944 |
0.76 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1460 |
1452 |
1.80 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1452 |
1444 |
3.53 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1448 |
1440 |
4.04 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1435 |
1428 |
0.63 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1374 |
1366 |
1.63 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1341 |
1333 |
7.01 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1301 |
1294 |
5.18 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1283 |
1276 |
8.05 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1237 |
1230 |
13.22 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1226 |
1219 |
36.27 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1133 |
1127 |
10.38 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1084 |
1078 |
7.01 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1075 |
1069 |
2.13 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1025 |
1019 |
2.48 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
984 |
978 |
14.34 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
929 |
924 |
2.28 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
877 |
872 |
7.36 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
761 |
756 |
6.97 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
701 |
697 |
38.88 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
576 |
573 |
32.40 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
423 |
420 |
3.60 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
390 |
387 |
6.83 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
324 |
322 |
4.37 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
243 |
241 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
232 |
230 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
146 |
145 |
2.09 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
114 |
113 |
1.32 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
74 |
73 |
3.28 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24389.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9945) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24255.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
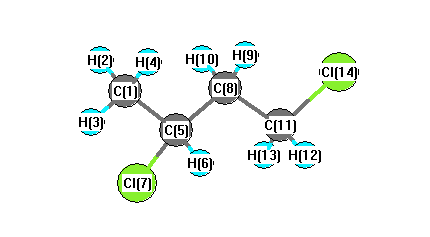
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.349 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.043 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Cl |
-0.213 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.120 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.110 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.119 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
C |
-0.161 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.132 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.158 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Cl |
-0.194 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.393 |
1.766 |
1.001 |
2.462 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-59.213 |
-3.810 |
0.071 |
| y |
-3.810 |
-50.758 |
0.054 |
| z |
0.071 |
0.054 |
-50.023 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-8.823 |
-3.810 |
0.071 |
| y |
-3.810 |
3.860 |
0.054 |
| z |
0.071 |
0.054 |
4.962 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 9.924 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -8.455 |
|---|
| xy | -3.810 |
|---|
| xz | 0.071 |
|---|
| yz | 0.054 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
12.735 |
0.298 |
-0.206 |
| y |
0.298 |
10.252 |
0.139 |
| z |
-0.206 |
0.139 |
8.182 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
377.285 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
19.424 |