Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3095 |
3078 |
3.14 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3048 |
3031 |
19.41 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3033 |
3016 |
36.90 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3029 |
3012 |
7.14 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3022 |
3005 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2993 |
2977 |
4.04 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2969 |
2952 |
24.50 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2959 |
2943 |
9.67 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1471 |
1463 |
4.77 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1462 |
1454 |
4.52 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1441 |
1433 |
2.43 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1436 |
1428 |
2.45 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1378 |
1370 |
1.15 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1352 |
1345 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1299 |
1292 |
6.24 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1281 |
1274 |
2.15 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1247 |
1240 |
12.15 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1201 |
1195 |
9.42 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1156 |
1149 |
16.14 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1086 |
1080 |
1.66 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1056 |
1051 |
0.96 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1031 |
1025 |
3.58 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
992 |
987 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
922 |
917 |
7.45 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
797 |
793 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
787 |
782 |
16.75 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
680 |
677 |
41.79 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
612 |
608 |
58.93 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
444 |
442 |
1.82 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
367 |
365 |
2.29 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
279 |
277 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
235 |
234 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
208 |
207 |
2.92 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
182 |
181 |
4.09 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
107 |
107 |
3.53 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
90 |
89 |
1.29 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24372.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9945) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24238.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
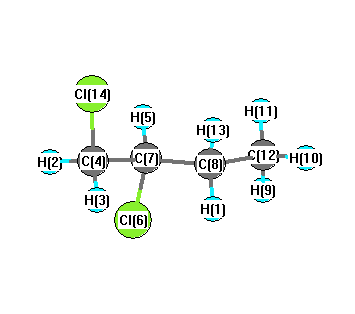
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
H |
0.100 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.153 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Cl |
-0.207 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
0.060 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.139 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.128 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.105 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.106 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
C |
-0.355 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Cl |
-0.188 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.331 |
0.684 |
0.271 |
0.806 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-57.372 |
3.359 |
-0.269 |
| y |
3.359 |
-50.814 |
-0.192 |
| z |
-0.269 |
-0.192 |
-50.323 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.804 |
3.359 |
-0.269 |
| y |
3.359 |
3.034 |
-0.192 |
| z |
-0.269 |
-0.192 |
3.770 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.539 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -6.558 |
|---|
| xy | 3.359 |
|---|
| xz | -0.269 |
|---|
| yz | -0.192 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
12.677 |
-0.961 |
0.159 |
| y |
-0.961 |
10.624 |
-0.100 |
| z |
0.159 |
-0.100 |
8.099 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
331.213 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
18.199 |