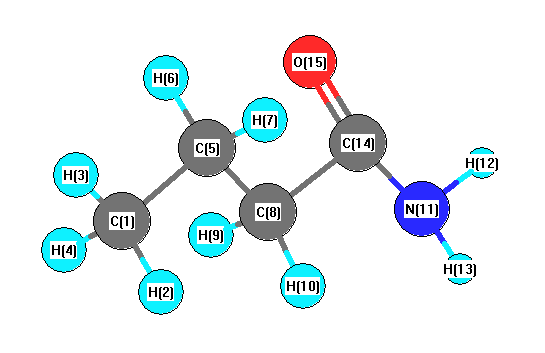
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3610 |
3595 |
18.67 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3477 |
3464 |
14.45 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3015 |
3003 |
57.91 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3010 |
2998 |
48.27 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2989 |
2977 |
8.25 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2965 |
2954 |
25.34 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2953 |
2941 |
37.19 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2945 |
2934 |
25.37 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2930 |
2919 |
12.85 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1701 |
1694 |
259.33 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1572 |
1566 |
88.10 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1476 |
1471 |
6.58 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1467 |
1462 |
7.02 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1461 |
1456 |
2.06 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1431 |
1425 |
6.19 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1380 |
1375 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1351 |
1346 |
39.46 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1319 |
1314 |
26.48 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1282 |
1277 |
42.19 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1234 |
1229 |
52.39 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1216 |
1211 |
19.70 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1100 |
1096 |
1.21 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1082 |
1078 |
2.74 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1034 |
1030 |
2.09 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1009 |
1005 |
3.65 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
893 |
889 |
2.39 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
865 |
862 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
810 |
806 |
5.03 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
735 |
732 |
3.97 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
656 |
654 |
5.01 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
596 |
594 |
12.94 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
506 |
504 |
6.51 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
412 |
410 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
331 |
330 |
1.92 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
241 |
240 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
192 |
191 |
169.59 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
183 |
183 |
18.66 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
91 |
90 |
1.86 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
44 |
44 |
3.69 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27781.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9961) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27672.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.285 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.098 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.105 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.094 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.212 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.106 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.246 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.099 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.414 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.216 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.212 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.302 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.329 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.379 |
-3.423 |
-0.055 |
3.444 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-33.501 |
-6.192 |
-0.350 |
| y |
-6.192 |
-39.480 |
-0.208 |
| z |
-0.350 |
-0.208 |
-38.480 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.479 |
-6.192 |
-0.350 |
| y |
-6.192 |
-3.490 |
-0.208 |
| z |
-0.350 |
-0.208 |
-1.990 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.980 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.979 |
|---|
| xy | -6.192 |
|---|
| xz | -0.350 |
|---|
| yz | -0.208 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.657 |
-0.453 |
-0.233 |
| y |
-0.453 |
8.776 |
0.055 |
| z |
-0.233 |
0.055 |
6.593 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
221.778 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.892 |