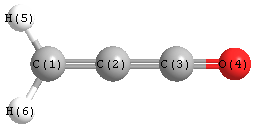Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.645543 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.645543 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 88.708195 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3072 |
2941 |
30.48 |
217.28 |
0.11 |
0.20 |
| 2 |
A1 |
2328 |
2229 |
984.57 |
46.54 |
0.50 |
0.66 |
| 3 |
A1 |
1803 |
1726 |
33.75 |
2.30 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 4 |
A1 |
1477 |
1414 |
2.22 |
11.34 |
0.58 |
0.73 |
| 5 |
A1 |
933 |
893 |
5.81 |
49.40 |
0.16 |
0.28 |
| 6 |
B1 |
1023 |
979 |
24.96 |
2.20 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 7 |
B1 |
656 |
628 |
18.94 |
0.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
B1 |
219 |
210 |
0.41 |
1.92 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
B2 |
3140 |
3006 |
5.98 |
135.64 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 10 |
B2 |
1062 |
1017 |
2.15 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
B2 |
469 |
449 |
8.28 |
2.59 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
B2 |
121i |
116i |
14.19 |
0.08 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 8030.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9573) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7687.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.866 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.554 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.718 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.888 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.923 |
-2.445 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-0.923 |
-2.445 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3122 | 2.5845 | 3.7546 | 1.0892 | 1.0892 |
C2 | 1.3122 | | 1.2723 | 2.4423 | 2.1041 | 2.1041 | C3 | 2.5845 | 1.2723 | | 1.1701 | 3.2951 | 3.2951 | O4 | 3.7546 | 2.4423 | 1.1701 | | 4.4305 | 4.4305 | H5 | 1.0892 | 2.1041 | 3.2951 | 4.4305 | | 1.8455 | H6 | 1.0892 | 2.1041 | 3.2951 | 4.4305 | 1.8455 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
180.000 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.096 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
122.096 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
180.000 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.808 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.315 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.811 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.140 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.687 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.788 |
2.788 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.695 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.476 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.867 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.524 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.194 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.718 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.437 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.220 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.642 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.121 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.137 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
81.977 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.054 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.646245 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.646245 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 88.921420 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3154 |
3020 |
5.81 |
117.71 |
0.71 |
0.83 |
| 2 |
A' |
3080 |
2948 |
28.66 |
177.61 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 3 |
A' |
2254 |
2158 |
997.58 |
51.38 |
0.52 |
0.68 |
| 4 |
A' |
1779 |
1703 |
10.74 |
4.44 |
0.23 |
0.37 |
| 5 |
A' |
1479 |
1416 |
1.05 |
11.28 |
0.62 |
0.77 |
| 6 |
A' |
1069 |
1024 |
16.75 |
3.00 |
0.05 |
0.09 |
| 7 |
A' |
953 |
912 |
3.34 |
42.66 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 8 |
A' |
505 |
484 |
12.60 |
4.22 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
A' |
148 |
142 |
22.22 |
5.28 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 10 |
A" |
1029 |
986 |
24.28 |
2.13 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A" |
700 |
670 |
13.79 |
0.39 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
A" |
265 |
254 |
0.97 |
2.47 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 8208.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9573) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7857.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.922 |
-1.575 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
-0.631 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.318 |
0.620 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
-0.784 |
1.687 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
1.989 |
-1.354 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.657 |
-2.629 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3190 | 2.5204 | 3.6808 | 1.0893 | 1.0875 |
C2 | 1.3190 | | 1.2907 | 2.4473 | 2.1159 | 2.1033 | C3 | 2.5204 | 1.2907 | | 1.1647 | 3.0359 | 3.3922 | O4 | 3.6808 | 2.4473 | 1.1647 | | 4.1154 | 4.5506 | H5 | 1.0893 | 2.1159 | 3.0359 | 4.1154 | | 1.8437 | H6 | 1.0875 | 2.1033 | 3.3922 | 4.5506 | 1.8437 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
149.919 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.666 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.559 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
170.681 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.775 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.302 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.202 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.427 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.640 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.157 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.156 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.739 |
-1.846 |
0.000 |
2.536 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-21.972 |
-0.849 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.849 |
-22.609 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.832 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.749 |
-0.849 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.849 |
-0.207 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.542 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.084 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.637 |
|---|
| xy | -0.849 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.684 |
-2.532 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.532 |
9.463 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.726 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
80.133 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.952 |