Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.834716 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.838721 |
| HF Energy | -169.834716 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.931321 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3841 |
3698 |
46.88 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3542 |
3410 |
2.42 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3020 |
2907 |
83.57 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1784 |
1717 |
195.27 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1448 |
1394 |
14.39 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1350 |
1299 |
176.18 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1209 |
1164 |
62.61 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1072 |
1032 |
215.57 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
624 |
601 |
1.11 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1046 |
1007 |
6.57 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
836 |
805 |
73.05 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
403 |
388 |
81.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10087.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9627) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9711.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.372 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.001 |
-0.534 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.197 |
-0.012 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.346 |
1.416 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.848 |
-0.081 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.820 |
0.791 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3504 | 1.2572 | 1.0999 | 1.9027 | 1.8676 |
O2 | 1.3504 | | 2.2590 | 2.0579 | 0.9611 | 3.1165 | N3 | 1.2572 | 2.2590 | | 2.1025 | 3.0457 | 1.0160 | H4 | 1.0999 | 2.0579 | 2.1025 | | 2.1209 | 2.2545 | H5 | 1.9027 | 0.9611 | 3.0457 | 2.1209 | | 3.7702 | H6 | 1.8676 | 3.1165 | 1.0160 | 2.2545 | 3.7702 | |
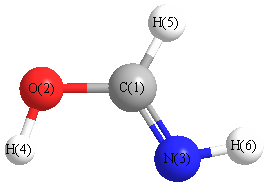 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
109.651 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
110.032 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
120.024 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
113.857 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
126.119 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.462 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.496 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.401 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.286 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.151 |
3.346 |
0.000 |
3.978 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-13.577 |
1.279 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.279 |
-17.845 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.729 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.710 |
1.279 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.279 |
-1.692 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.018 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.036 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.268 |
|---|
| xy | 1.279 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.858 |
-0.012 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.012 |
2.935 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.722 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.085 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.410 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.845754 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.849930 |
| HF Energy | -169.845754 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.314385 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3733 |
3593 |
29.24 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3544 |
3412 |
2.22 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3113 |
2997 |
43.72 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1754 |
1688 |
273.96 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1415 |
1363 |
26.85 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1388 |
1336 |
2.39 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1215 |
1170 |
116.42 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1083 |
1042 |
179.08 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
590 |
568 |
55.21 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1056 |
1017 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
838 |
807 |
27.58 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
665 |
640 |
219.53 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10196.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9627) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9816.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.416 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.109 |
-0.336 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.155 |
-0.092 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.270 |
1.476 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.819 |
-1.261 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.874 |
0.624 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3398 | 1.2617 | 1.0934 | 1.8659 | 1.8858 |
O2 | 1.3398 | | 2.2763 | 1.9966 | 0.9688 | 3.1337 | N3 | 1.2617 | 2.2763 | | 2.1185 | 2.2931 | 1.0157 | H4 | 1.0934 | 1.9966 | 2.1185 | | 2.7908 | 2.3070 | H5 | 1.8659 | 0.9688 | 2.2931 | 2.7908 | | 3.2871 | H6 | 1.8858 | 3.1337 | 1.0157 | 2.3070 | 3.2871 | |
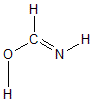 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
106.748 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
111.347 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
122.065 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.875 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
128.060 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.133 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.483 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.551 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.401 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.296 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.133 |
0.988 |
0.000 |
0.997 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.476 |
3.469 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.469 |
-13.857 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.721 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.187 |
3.469 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.469 |
5.241 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.054 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.108 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.619 |
|---|
| xy | 3.469 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.351 |
0.072 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.072 |
3.336 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.708 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.417 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.357 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.839752 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.843862 |
| HF Energy | -169.839752 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.836057 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3766 |
3626 |
16.52 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3451 |
3322 |
9.45 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3180 |
3061 |
16.53 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1750 |
1685 |
282.82 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1423 |
1370 |
0.49 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1360 |
1309 |
26.50 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1134 |
1092 |
295.01 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1093 |
1052 |
31.38 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
593 |
571 |
37.73 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1080 |
1040 |
80.95 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
854 |
823 |
59.30 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
547 |
527 |
89.32 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10115.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9627) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9738.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.435 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.099 |
-0.353 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.223 |
0.129 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.307 |
1.480 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.840 |
-1.284 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.382 |
-0.881 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3528 | 1.2606 | 1.0887 | 1.9133 | 1.9089 |
O2 | 1.3528 | | 2.3717 | 1.9968 | 0.9660 | 2.5372 | N3 | 1.2606 | 2.3717 | | 2.0408 | 2.5004 | 1.0227 | H4 | 1.0887 | 1.9968 | 2.0408 | | 2.8144 | 2.9030 | H5 | 1.9133 | 0.9660 | 2.5004 | 2.8144 | | 2.2587 | H6 | 1.9089 | 2.5372 | 1.0227 | 2.9030 | 2.2587 | |
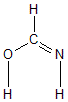 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
110.085 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
113.030 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
130.298 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.267 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.435 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.119 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.484 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.517 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.235 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.385 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.262 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.949 |
-2.055 |
0.000 |
2.263 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.093 |
-1.956 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.956 |
-12.784 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.707 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.347 |
-1.956 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.956 |
8.116 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.769 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.537 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.308 |
|---|
| xy | -1.956 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.174 |
-0.138 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.138 |
3.494 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.730 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.075 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.409 |


