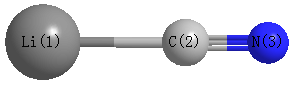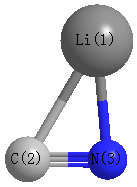Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.332945 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.331990 |
| HF Energy | -100.332945 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 27.562515 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.076 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.150 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.018 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 1.9265 | 3.0946 |
C2 | 1.9265 | | 1.1681 | N3 | 3.0946 | 1.1681 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.491 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.050 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.441 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-8.887 |
8.887 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.079 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-14.079 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.702 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.890 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-7.890 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
15.781 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 31.561 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.290 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.290 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.326 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
25.834 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
5.083 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.338517 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.337799 |
| HF Energy | -100.338517 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 29.190094 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
1.430 |
-0.613 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.715 |
-0.365 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.576 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 2.1598 | 1.8598 |
C2 | 2.1598 | | 1.1819 | N3 | 1.8598 | 1.1819 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
59.352 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
87.506 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
33.142 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.414 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.055 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.469 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
6.388 |
-2.589 |
0.000 |
6.893 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-5.770 |
-5.925 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.925 |
-15.014 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-14.484 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
8.980 |
-5.925 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.925 |
-4.887 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.092 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -8.185 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 9.245 |
|---|
| xy | -5.925 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.197 |
0.356 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.356 |
3.208 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.507 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
20.797 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.560 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.334956 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -100.334956 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 28.255327 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.893 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.073 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.108 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 2.9653 | 1.7840 |
C2 | 2.9653 | | 1.1813 | N3 | 1.7840 | 1.1813 | |
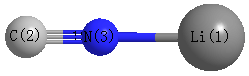 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.592 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.080 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.512 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.603 |
8.603 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.012 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-14.012 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.543 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.234 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-6.234 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.469 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 24.938 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.218 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.218 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.387 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
23.889 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.888 |