Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -133.269195 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -133.273373 |
| HF Energy | -133.269195 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.945767 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3503 |
3333 |
0.70 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3313 |
3153 |
3.89 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3200 |
3044 |
3.24 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3087 |
2937 |
47.79 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1533 |
1459 |
8.74 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1476 |
1405 |
2.40 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1374 |
1307 |
34.67 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1269 |
1208 |
9.28 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1127 |
1072 |
22.78 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1001 |
953 |
9.92 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
488 |
464 |
11.69 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
1056 |
1005 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
812 |
772 |
10.24 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
683 |
650 |
112.96 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
532 |
506 |
5.30 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12226.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9515) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11633.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.418 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
1.150 |
-0.376 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.190 |
-0.136 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.142 |
1.504 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.141 |
0.061 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.050 |
-1.455 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.905 |
0.594 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.3976 | 1.3126 | 1.0960 | 2.1702 | 2.1468 | 1.9128 |
C2 | 1.3976 | | 2.3527 | 2.1336 | 1.0828 | 1.0835 | 3.2053 | N3 | 1.3126 | 2.3527 | | 2.1134 | 3.3368 | 2.5994 | 1.0214 | H4 | 1.0960 | 2.1336 | 2.1134 | | 2.4649 | 3.0954 | 2.2405 | H5 | 2.1702 | 1.0828 | 3.3368 | 2.4649 | | 1.8680 | 4.0804 | H6 | 2.1468 | 1.0835 | 2.5994 | 3.0954 | 1.8680 | | 3.5953 | H7 | 1.9128 | 3.2053 | 1.0214 | 2.2405 | 4.0804 | 3.5953 | |
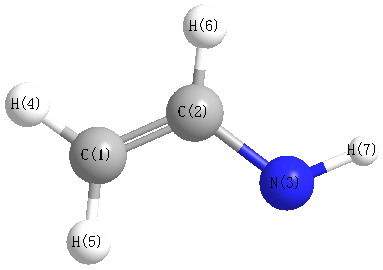 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
H5 |
121.558 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H6 |
119.287 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H7 |
109.444 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
120.440 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.146 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
122.414 |
| H5 |
C2 |
H6 |
119.155 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.064 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.245 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.484 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.141 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.158 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.251 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.041 |
1.598 |
0.000 |
1.907 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-16.472 |
-2.811 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.811 |
-17.352 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.772 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.090 |
-2.811 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.811 |
0.770 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.860 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.721 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.880 |
|---|
| xy | -2.811 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.320 |
-0.416 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.416 |
4.032 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.799 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.107 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.716 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -133.268808 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -133.272969 |
| HF Energy | -133.268808 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.939194 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3453 |
3286 |
8.56 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3293 |
3133 |
7.67 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3183 |
3028 |
3.77 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3151 |
2998 |
23.45 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1517 |
1443 |
4.94 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1470 |
1399 |
3.27 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1399 |
1331 |
13.34 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1256 |
1195 |
33.05 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1154 |
1098 |
33.98 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
994 |
946 |
0.98 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
495 |
471 |
8.30 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
1087 |
1034 |
48.92 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
820 |
780 |
70.01 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
686 |
653 |
7.32 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
491 |
467 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12223.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9515) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11630.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.447 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
1.127 |
-0.382 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.256 |
0.068 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.168 |
1.526 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.130 |
0.028 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.022 |
-1.462 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.294 |
-0.957 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.3992 | 1.3118 | 1.0918 | 2.1709 | 2.1657 | 1.9086 |
C2 | 1.3992 | | 2.4255 | 2.1352 | 1.0834 | 1.0857 | 2.4883 | N3 | 1.3118 | 2.4255 | | 2.0376 | 3.3863 | 2.7444 | 1.0251 | H4 | 1.0918 | 2.1352 | 2.0376 | | 2.4683 | 3.1078 | 2.8804 | H5 | 2.1709 | 1.0834 | 3.3863 | 2.4683 | | 1.8575 | 3.5626 | H6 | 2.1657 | 1.0857 | 2.7444 | 3.1078 | 1.8575 | | 2.3703 | H7 | 1.9086 | 2.4883 | 1.0251 | 2.8804 | 3.5626 | 2.3703 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
H5 |
121.436 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H6 |
120.747 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H7 |
108.895 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
126.897 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.471 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
115.632 |
| H5 |
C2 |
H6 |
117.817 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.081 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.273 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.477 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.142 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.242 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.135 |
-1.105 |
0.000 |
2.404 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-20.417 |
2.115 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.115 |
-15.977 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.784 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.537 |
2.115 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.115 |
4.123 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.586 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.173 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.440 |
|---|
| xy | 2.115 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.993 |
-0.074 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.074 |
4.219 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.804 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.135 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.718 |
