Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3220 |
3064 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3215 |
3059 |
0.87 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3188 |
3034 |
6.09 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3169 |
3015 |
7.91 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3158 |
3005 |
7.55 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3105 |
2954 |
3.80 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3101 |
2951 |
1.66 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3086 |
2936 |
15.41 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1519 |
1445 |
8.81 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1513 |
1439 |
9.81 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1474 |
1403 |
10.53 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1470 |
1399 |
3.76 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1465 |
1394 |
4.41 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1427 |
1358 |
2.03 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1366 |
1300 |
54.95 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1358 |
1292 |
153.80 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1317 |
1253 |
29.62 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1273 |
1211 |
7.40 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1156 |
1100 |
149.42 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1096 |
1043 |
2.64 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1073 |
1021 |
6.43 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1006 |
957 |
3.72 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
980 |
932 |
30.81 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
973 |
925 |
12.53 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
809 |
770 |
59.42 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
739 |
703 |
22.02 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
662 |
630 |
13.24 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
499 |
475 |
20.72 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
443 |
422 |
30.07 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
401 |
382 |
7.92 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
312 |
297 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
283 |
269 |
1.51 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
227 |
216 |
2.09 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
208 |
198 |
1.07 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
198 |
188 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
87 |
83 |
2.67 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25287.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9515) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24060.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
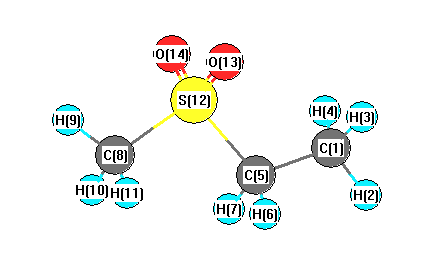
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.418 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.156 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.142 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.462 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.181 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.596 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.210 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
S |
1.125 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
O |
-0.550 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.545 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
3.074 |
2.842 |
-2.193 |
4.726 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-43.587 |
-5.194 |
-1.260 |
| y |
-5.194 |
-41.362 |
-0.601 |
| z |
-1.260 |
-0.601 |
-47.603 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.896 |
-5.194 |
-1.260 |
| y |
-5.194 |
4.233 |
-0.601 |
| z |
-1.260 |
-0.601 |
-5.129 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -10.257 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.225 |
|---|
| xy | -5.194 |
|---|
| xz | -1.260 |
|---|
| yz | -0.601 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
191.201 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.828 |