Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -133.276843 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -133.281019 |
| HF Energy | -133.276843 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.901634 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3518 |
3349 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3311 |
3151 |
2.79 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3197 |
3043 |
3.18 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3092 |
2943 |
45.36 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1526 |
1452 |
6.64 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1473 |
1402 |
2.02 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1369 |
1303 |
31.22 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1264 |
1203 |
6.95 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1121 |
1067 |
23.31 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1002 |
954 |
10.12 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
489 |
465 |
13.59 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
1049 |
999 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
824 |
784 |
15.11 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
680 |
647 |
129.27 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
525 |
499 |
6.30 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12219.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9518) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11630.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.417 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
1.153 |
-0.376 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.191 |
-0.135 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.135 |
1.504 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.141 |
0.066 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.056 |
-1.456 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.911 |
0.588 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.3993 | 1.3128 | 1.0957 | 2.1697 | 2.1502 | 1.9185 |
C2 | 1.3993 | | 2.3563 | 2.1384 | 1.0831 | 1.0839 | 3.2118 | N3 | 1.3128 | 2.3563 | | 2.1085 | 3.3385 | 2.6069 | 1.0204 | H4 | 1.0957 | 2.1384 | 2.1085 | | 2.4684 | 3.1003 | 2.2414 | H5 | 2.1697 | 1.0831 | 3.3385 | 2.4684 | | 1.8694 | 4.0855 | H6 | 2.1502 | 1.0839 | 2.6069 | 3.1003 | 1.8694 | | 3.6032 | H7 | 1.9185 | 3.2118 | 1.0204 | 2.2414 | 4.0855 | 3.6032 | |
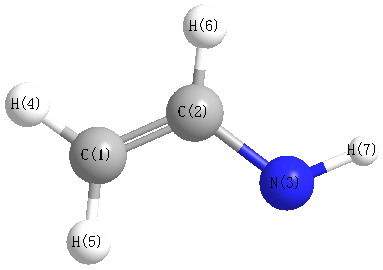 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
H5 |
121.346 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H6 |
119.427 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H7 |
109.992 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
120.610 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.460 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
121.930 |
| H5 |
C2 |
H6 |
119.227 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.230 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.150 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.380 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.265 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.154 |
1.761 |
0.000 |
2.106 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-16.986 |
-3.118 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.118 |
-17.863 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-20.621 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.256 |
-3.118 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.118 |
0.940 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.197 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.393 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.878 |
|---|
| xy | -3.118 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.966 |
-0.300 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.300 |
4.540 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.063 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.577 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.751 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -133.275613 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -133.279772 |
| HF Energy | -133.275613 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.896293 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3466 |
3299 |
4.95 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3291 |
3133 |
6.31 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3181 |
3027 |
3.75 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3159 |
3007 |
19.64 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1510 |
1437 |
5.48 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1465 |
1394 |
3.25 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1389 |
1322 |
6.69 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1249 |
1189 |
28.66 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1148 |
1093 |
34.33 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
990 |
943 |
1.18 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
494 |
470 |
9.32 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
1080 |
1028 |
59.18 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
826 |
787 |
80.20 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
683 |
650 |
7.21 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
486 |
462 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12208.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9518) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11620.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.449 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
1.128 |
-0.381 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.256 |
0.065 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.164 |
1.528 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.130 |
0.031 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.023 |
-1.462 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.298 |
-0.958 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.4010 | 1.3130 | 1.0910 | 2.1709 | 2.1680 | 1.9146 |
C2 | 1.4010 | | 2.4255 | 2.1388 | 1.0837 | 1.0860 | 2.4944 | N3 | 1.3130 | 2.4255 | | 2.0381 | 3.3862 | 2.7436 | 1.0242 | H4 | 1.0910 | 2.1388 | 2.0381 | | 2.4710 | 3.1110 | 2.8839 | H5 | 2.1709 | 1.0837 | 3.3862 | 2.4710 | | 1.8592 | 3.5687 | H6 | 2.1680 | 1.0860 | 2.7436 | 3.1110 | 1.8592 | | 2.3759 | H7 | 1.9146 | 2.4944 | 1.0242 | 2.8839 | 3.5687 | 2.3759 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
H5 |
121.259 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H6 |
120.799 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H7 |
109.389 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
126.657 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.710 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
115.633 |
| H5 |
C2 |
H6 |
117.942 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.115 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.270 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.361 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.171 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.249 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.335 |
-1.168 |
0.000 |
2.611 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-21.287 |
2.375 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.375 |
-16.250 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-20.577 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.874 |
2.375 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.375 |
4.682 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.809 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.617 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.038 |
|---|
| xy | 2.375 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.862 |
-0.290 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.290 |
4.558 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.061 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.577 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.751 |
