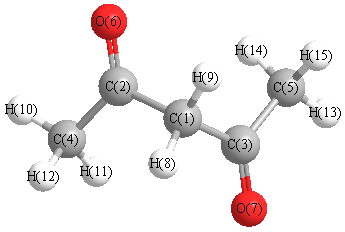
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3195 |
3034 |
5.59 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3137 |
2979 |
2.54 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3133 |
2975 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3072 |
2917 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1789 |
1699 |
11.21 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1539 |
1462 |
26.05 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1531 |
1453 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1507 |
1431 |
20.89 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1440 |
1368 |
6.71 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1291 |
1226 |
31.72 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1169 |
1110 |
6.25 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1128 |
1071 |
4.09 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
963 |
915 |
1.12 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
801 |
761 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
648 |
615 |
1.47 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
480 |
455 |
5.39 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
342 |
324 |
1.14 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
215 |
204 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
157 |
149 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
75 |
71 |
6.68 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3211 |
3050 |
1.86 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3195 |
3034 |
4.06 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
3136 |
2978 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
3071 |
2916 |
2.39 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1765 |
1676 |
189.27 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1538 |
1461 |
9.14 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1525 |
1448 |
33.75 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1441 |
1368 |
137.60 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1289 |
1224 |
70.36 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1193 |
1133 |
235.91 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
1086 |
1031 |
16.22 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
1050 |
997 |
0.97 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
909 |
864 |
33.37 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
800 |
760 |
9.51 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
550 |
522 |
21.92 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
515 |
489 |
6.43 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
B |
430 |
408 |
0.85 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
B |
215 |
204 |
1.64 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
B |
57 |
54 |
12.51 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27293.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9496) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25918.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.616 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.438 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.438 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.711 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.711 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.447 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
O |
-0.447 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.262 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.262 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.253 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.263 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.249 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.253 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.263 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.249 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.469 |
1.469 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-43.132 |
-8.814 |
0.000 |
| y |
-8.814 |
-45.952 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-40.209 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.051 |
-8.814 |
0.000 |
| y |
-8.814 |
-4.281 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.333 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.665 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.820 |
|---|
| xy | -8.814 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.387 |
-0.192 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.192 |
8.190 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.252 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
222.868 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.929 |