Jump to
S2C1
Energy calculated at LSDA/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2609.649414 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2609.652145 |
| HF Energy | -2609.649414 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.861081 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at LSDA/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.027 |
1.535 |
0.000 |
| Br2 |
0.027 |
-0.313 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.088 |
1.740 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
| C1 | | 1.8481 | 1.1336 |
Br2 | 1.8481 | | 2.3360 | H3 | 1.1336 | 2.3360 | |
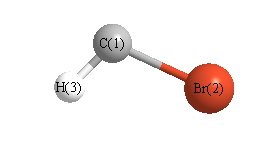 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
100.400 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.361 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.389 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.028 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.306 |
-1.004 |
0.000 |
1.647 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.576 |
-3.096 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.096 |
-26.314 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.974 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.432 |
-3.096 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.096 |
-1.539 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.971 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.942 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.738 |
|---|
| xy | -3.096 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.579 |
-0.043 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.043 |
7.389 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.980 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
37.602 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.132 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at LSDA/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2609.640879 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2609.643585 |
| HF Energy | -2609.640879 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.785130 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at LSDA/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.021 |
1.482 |
0.000 |
| Br2 |
0.021 |
-0.315 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-0.864 |
2.143 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
| C1 | | 1.7975 | 1.1044 |
Br2 | 1.7975 | | 2.6129 | H3 | 1.1044 | 2.6129 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.194 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.429 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.236 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.758 |
-0.169 |
0.000 |
0.776 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.407 |
-1.883 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.883 |
-22.884 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-25.764 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.083 |
-1.883 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.883 |
2.201 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.118 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.236 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.523 |
|---|
| xy | -1.883 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.164 |
-0.093 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.093 |
7.098 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.125 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
37.229 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.102 |
