Vibrational Frequencies calculated at LSDA/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3630 |
3562 |
41.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3503 |
3438 |
22.69 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3089 |
3031 |
1.62 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3064 |
3007 |
4.38 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3013 |
2956 |
2.10 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3005 |
2949 |
50.51 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2949 |
2894 |
67.79 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2922 |
2868 |
61.40 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1795 |
1762 |
325.03 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1560 |
1531 |
288.10 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1512 |
1484 |
47.71 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1448 |
1421 |
26.04 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1442 |
1415 |
30.56 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1439 |
1412 |
23.16 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1427 |
1401 |
38.43 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1389 |
1363 |
13.86 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1355 |
1330 |
34.96 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1333 |
1308 |
10.30 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1253 |
1230 |
37.97 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1132 |
1111 |
2.49 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1088 |
1067 |
4.50 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1067 |
1047 |
18.03 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1049 |
1029 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1026 |
1007 |
51.99 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
786 |
771 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
750 |
736 |
47.48 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
597 |
585 |
5.45 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
553 |
543 |
186.57 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
500 |
491 |
3.94 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
445 |
437 |
36.03 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
379 |
372 |
16.28 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
316 |
310 |
17.02 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
196 |
193 |
3.43 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
169 |
166 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
149 |
147 |
5.62 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
108 |
106 |
4.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25719.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9813) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25238.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
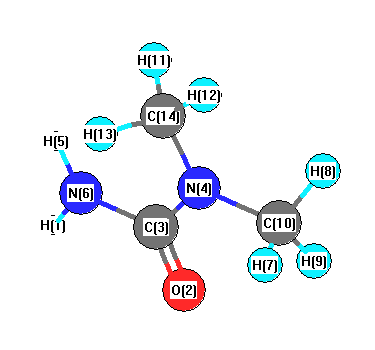
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
H |
0.300 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.475 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.590 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.342 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.279 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
N |
-0.651 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.140 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.140 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.190 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
C |
-0.310 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.155 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
-0.322 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.478 |
3.261 |
1.064 |
3.735 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-33.053 |
4.599 |
2.009 |
| y |
4.599 |
-36.914 |
1.321 |
| z |
2.009 |
1.321 |
-37.207 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.008 |
4.599 |
2.009 |
| y |
4.599 |
-1.784 |
1.321 |
| z |
2.009 |
1.321 |
-2.224 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.448 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.861 |
|---|
| xy | 4.599 |
|---|
| xz | 2.009 |
|---|
| yz | 1.321 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.207 |
0.004 |
-0.050 |
| y |
0.004 |
8.234 |
0.239 |
| z |
-0.050 |
0.239 |
5.125 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |