Vibrational Frequencies calculated at LSDA/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3650 |
3595 |
43.46 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3504 |
3451 |
33.16 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3073 |
3027 |
13.19 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3071 |
3025 |
2.23 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3069 |
3023 |
22.66 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3069 |
3022 |
11.86 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2979 |
2934 |
15.97 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2978 |
2933 |
26.36 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2956 |
2912 |
34.17 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1767 |
1741 |
282.72 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1547 |
1524 |
176.10 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1452 |
1430 |
30.58 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1431 |
1410 |
15.24 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1421 |
1399 |
3.53 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1412 |
1391 |
3.14 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1384 |
1363 |
56.82 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1343 |
1323 |
13.99 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1328 |
1308 |
15.57 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1272 |
1253 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1242 |
1223 |
44.29 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1158 |
1141 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1114 |
1098 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1092 |
1075 |
5.12 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1017 |
1002 |
9.57 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
951 |
936 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
923 |
909 |
4.33 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
892 |
879 |
3.09 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
757 |
746 |
4.22 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
755 |
744 |
3.49 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
598 |
589 |
4.50 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
594 |
585 |
14.90 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
463 |
456 |
2.44 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
321 |
316 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
316 |
312 |
188.32 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
286 |
281 |
3.85 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
242 |
238 |
7.50 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
238 |
234 |
1.63 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
207 |
204 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
29 |
28 |
8.23 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27948.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27529.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
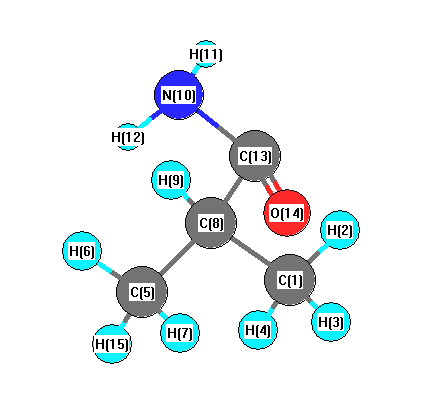
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.638 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.187 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.219 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.182 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.638 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.187 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.219 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
N |
-0.515 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.334 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.307 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
C |
0.307 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.477 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.182 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.292 |
-0.001 |
-3.765 |
3.776 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-33.091 |
0.001 |
4.878 |
| y |
0.001 |
-39.108 |
0.001 |
| z |
4.878 |
0.001 |
-40.142 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.533 |
0.001 |
4.878 |
| y |
0.001 |
-2.491 |
0.001 |
| z |
4.878 |
0.001 |
-4.042 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -8.084 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.016 |
|---|
| xy | 0.001 |
|---|
| xz | 4.878 |
|---|
| yz | 0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.298 |
0.000 |
0.386 |
| y |
0.000 |
8.309 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.386 |
0.000 |
9.239 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |