Vibrational Frequencies calculated at SVWN/cc-pVQZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3485 |
3485 |
1.22 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3399 |
3399 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3009 |
3009 |
21.46 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3004 |
3004 |
30.39 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3002 |
3002 |
33.70 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3001 |
3001 |
34.81 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2983 |
2983 |
40.67 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2946 |
2946 |
54.51 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2940 |
2940 |
8.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
2932 |
2932 |
20.31 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
2924 |
2924 |
41.08 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
2914 |
2914 |
13.94 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
2898 |
2898 |
1.98 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1572 |
1572 |
37.96 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1418 |
1418 |
4.06 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1405 |
1405 |
22.20 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1402 |
1402 |
8.15 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1401 |
1401 |
3.92 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1392 |
1392 |
3.56 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1359 |
1359 |
7.24 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1326 |
1326 |
2.05 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1320 |
1320 |
2.23 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1318 |
1318 |
3.96 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1309 |
1309 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1294 |
1294 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1273 |
1273 |
0.59 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1248 |
1248 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
1236 |
1236 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
1232 |
1232 |
2.36 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
1183 |
1183 |
3.15 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
1159 |
1159 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
1131 |
1131 |
7.69 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
1114 |
1114 |
1.97 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
1059 |
1059 |
1.57 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
1031 |
1031 |
2.19 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
1028 |
1028 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
1021 |
1021 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
972 |
972 |
1.56 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
924 |
924 |
9.97 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A |
874 |
874 |
3.47 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A |
869 |
869 |
8.20 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A |
844 |
844 |
16.48 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A |
802 |
802 |
123.48 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A |
781 |
781 |
28.11 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A |
761 |
761 |
0.98 |
|
|
|
| 46 |
A |
534 |
534 |
1.76 |
|
|
|
| 47 |
A |
447 |
447 |
1.11 |
|
|
|
| 48 |
A |
439 |
439 |
2.94 |
|
|
|
| 49 |
A |
397 |
397 |
0.14 |
|
|
|
| 50 |
A |
333 |
333 |
10.56 |
|
|
|
| 51 |
A |
324 |
324 |
2.28 |
|
|
|
| 52 |
A |
242 |
242 |
15.37 |
|
|
|
| 53 |
A |
213 |
213 |
18.61 |
|
|
|
| 54 |
A |
157 |
157 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 39790.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 39790.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/cc-pVQZ
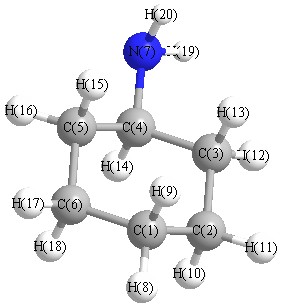
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.202 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.195 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.188 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.031 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.177 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.210 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.335 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.088 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.088 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.119 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.069 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.111 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.074 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
H |
0.129 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.593 |
0.932 |
0.486 |
1.206 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-48.241 |
-3.517 |
-1.711 |
| y |
-3.517 |
-46.630 |
-0.840 |
| z |
-1.711 |
-0.840 |
-45.166 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.343 |
-3.517 |
-1.711 |
| y |
-3.517 |
0.074 |
-0.840 |
| z |
-1.711 |
-0.840 |
2.270 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.539 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.611 |
|---|
| xy | -3.517 |
|---|
| xz | -1.711 |
|---|
| yz | -0.840 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
13.513 |
-0.095 |
-0.158 |
| y |
-0.095 |
12.421 |
-0.005 |
| z |
-0.158 |
-0.005 |
11.053 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
228.139 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.104 |