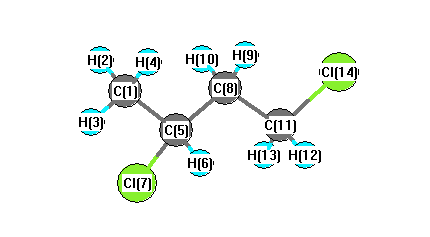
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at SVWN/TZVP
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3077 |
3042 |
5.04 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3076 |
3041 |
2.52 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3055 |
3020 |
8.28 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3020 |
2986 |
7.68 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3009 |
2974 |
7.64 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2997 |
2963 |
4.16 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2975 |
2941 |
9.61 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2966 |
2932 |
3.41 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1422 |
1405 |
6.88 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1421 |
1405 |
6.29 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1412 |
1396 |
13.56 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1395 |
1379 |
2.52 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1351 |
1336 |
25.74 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1343 |
1327 |
10.38 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1285 |
1270 |
8.64 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1268 |
1253 |
7.52 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1231 |
1216 |
15.14 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1214 |
1200 |
14.33 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1151 |
1138 |
11.38 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1112 |
1099 |
2.14 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1096 |
1083 |
4.82 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1067 |
1055 |
6.58 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1006 |
995 |
15.77 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
930 |
920 |
1.90 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
904 |
893 |
5.77 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
773 |
764 |
29.00 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
761 |
753 |
11.01 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
626 |
618 |
23.68 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
432 |
427 |
2.29 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
408 |
404 |
4.95 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
333 |
329 |
3.50 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
255 |
252 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
244 |
241 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
147 |
145 |
2.30 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
120 |
119 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
75 |
74 |
3.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24477.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9885) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24195.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/TZVP
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.451 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.181 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.288 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.236 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Cl |
-0.084 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.363 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.188 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.202 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
C |
-0.329 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.215 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Cl |
-0.080 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.408 |
1.710 |
1.002 |
2.431 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-58.966 |
-3.552 |
0.034 |
| y |
-3.552 |
-51.463 |
0.169 |
| z |
0.034 |
0.169 |
-50.845 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.812 |
-3.552 |
0.034 |
| y |
-3.552 |
3.442 |
0.169 |
| z |
0.034 |
0.169 |
4.370 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.740 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -7.503 |
|---|
| xy | -3.552 |
|---|
| xz | 0.034 |
|---|
| yz | 0.169 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
12.875 |
0.210 |
-0.226 |
| y |
0.210 |
10.680 |
0.110 |
| z |
-0.226 |
0.110 |
8.690 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
358.784 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
18.942 |