Vibrational Frequencies calculated at SVWN/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3716 |
3679 |
17.11 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3526 |
3492 |
6.26 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3435 |
3401 |
1.46 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3012 |
2983 |
19.96 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2934 |
2905 |
52.66 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1585 |
1570 |
29.79 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1425 |
1411 |
0.70 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1356 |
1343 |
30.58 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1324 |
1311 |
2.48 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1309 |
1296 |
3.20 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1152 |
1141 |
55.08 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1096 |
1085 |
12.81 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1002 |
992 |
205.33 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
875 |
866 |
3.01 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
751 |
743 |
174.39 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
469 |
465 |
59.28 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
406 |
402 |
87.29 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
264 |
261 |
71.22 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14816.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9903) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14673.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
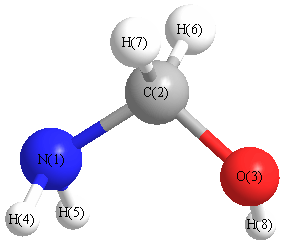
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.316 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.028 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.301 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.077 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.179 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.479 |
-1.175 |
1.202 |
1.748 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.264 |
-1.363 |
-1.740 |
| y |
-1.363 |
-17.488 |
-1.373 |
| z |
-1.740 |
-1.373 |
-16.927 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.057 |
-1.363 |
-1.740 |
| y |
-1.363 |
2.608 |
-1.373 |
| z |
-1.740 |
-1.373 |
3.449 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.898 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.776 |
|---|
| xy | -1.363 |
|---|
| xz | -1.740 |
|---|
| yz | -1.373 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.460 |
-0.069 |
-0.109 |
| y |
-0.069 |
4.123 |
-0.135 |
| z |
-0.109 |
-0.135 |
3.966 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
49.288 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.021 |