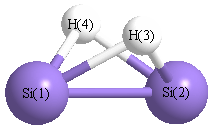Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.787796 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.787796 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 66.883719 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2337 |
2247 |
0.00 |
320.18 |
0.30 |
0.46 |
| 2 |
Σg |
772 |
743 |
0.00 |
164.11 |
0.08 |
0.14 |
| 3 |
Σu |
2332 |
2243 |
2.78 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 4 |
Πg |
575i |
553i |
0.00 |
17.57 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
Πg |
575i |
553i |
0.00 |
17.57 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
Πu |
441 |
424 |
6.74 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Πu |
441 |
424 |
6.74 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2587.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9616) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2487.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.989 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.989 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.461 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.461 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9787 | 1.4721 | 3.4508 |
Si2 | 1.9787 | | 3.4508 | 1.4721 | H3 | 1.4721 | 3.4508 | | 4.9229 | H4 | 3.4508 | 1.4721 | 4.9229 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
-0.293 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.293 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.293 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.293 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.431 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-30.431 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.950 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-5.240 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-5.240 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.481 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 20.961 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.322 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
9.322 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
15.561 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.349 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.507 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.817242 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.817242 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.967543 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2171 |
2088 |
0.00 |
416.69 |
0.44 |
0.61 |
| 2 |
Ag |
618 |
594 |
0.00 |
63.93 |
0.21 |
0.34 |
| 3 |
Ag |
567 |
545 |
0.00 |
62.81 |
0.06 |
0.12 |
| 4 |
Au |
218 |
210 |
57.15 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Bu |
2176 |
2093 |
98.85 |
0.00 |
0.44 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
Bu |
190 |
183 |
55.30 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2970.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9616) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2856.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
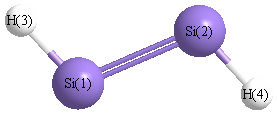
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.050 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.050 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.216 |
1.935 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.216 |
-1.935 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.0994 | 1.5042 | 3.2231 |
Si2 | 2.0994 | | 3.2231 | 1.5042 | H3 | 1.5042 | 3.2231 | | 4.5711 | H4 | 3.2231 | 1.5042 | 4.5711 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
126.070 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
126.070 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
-0.115 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.115 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.923 |
-0.084 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.084 |
-22.646 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.172 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.014 |
-0.084 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.084 |
7.401 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-5.388 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -10.775 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -6.277 |
|---|
| xy | -0.084 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.198 |
0.172 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.172 |
16.340 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.295 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
58.526 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.650 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.853121 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.853121 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.361588 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1615 |
1553 |
1.79 |
88.47 |
0.03 |
0.05 |
| 2 |
A1 |
921 |
886 |
24.37 |
2.09 |
0.10 |
0.17 |
| 3 |
A1 |
533 |
513 |
0.22 |
72.14 |
0.18 |
0.30 |
| 4 |
A2 |
1098 |
1056 |
0.00 |
9.74 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B1 |
1552 |
1492 |
5.57 |
10.37 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
1162 |
1118 |
375.10 |
1.24 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3440.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9616) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3308.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.112 |
-0.053 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.112 |
-0.053 |
| H3 |
1.000 |
0.000 |
0.746 |
| H4 |
-1.000 |
0.000 |
0.746 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.2246 | 1.6960 | 1.6960 |
Si2 | 2.2246 | | 1.6960 | 1.6960 | H3 | 1.6960 | 1.6960 | | 2.0005 | H4 | 1.6960 | 1.6960 | 2.0005 | |
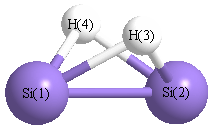 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
49.019 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.019 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
-0.078 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.078 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.078 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.078 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.499 |
0.499 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.190 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-31.787 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-29.103 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.255 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.141 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.115 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.229 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.597 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.124 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
14.170 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.497 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
55.964 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.481 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.835582 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.835582 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.834718 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2171 |
2087 |
79.23 |
336.20 |
0.36 |
0.53 |
| 2 |
A' |
1651 |
1588 |
44.59 |
77.79 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
| 3 |
A' |
1072 |
1031 |
122.26 |
4.91 |
0.47 |
0.64 |
| 4 |
A' |
630 |
605 |
19.03 |
96.73 |
0.10 |
0.18 |
| 5 |
A' |
464 |
446 |
4.23 |
2.87 |
0.25 |
0.40 |
| 6 |
A" |
181 |
174 |
40.42 |
3.16 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3084.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9616) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2965.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.060 |
-1.146 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.060 |
0.975 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.267 |
-0.014 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.420 |
2.399 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1209 | 1.7440 | 3.5775 |
Si2 | 2.1209 | | 1.6552 | 1.5030 | H3 | 1.7440 | 1.6552 | | 2.5577 | H4 | 3.5775 | 1.5030 | 2.5577 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
161.365 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.546 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
-0.009 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.250 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.074 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.186 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.100 |
0.961 |
0.000 |
0.966 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.050 |
0.224 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.224 |
-25.368 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.224 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.246 |
0.224 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.224 |
3.769 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-5.015 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -10.030 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.682 |
|---|
| xy | 0.224 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.332 |
-0.074 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.074 |
15.186 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.546 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.744 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.533 |