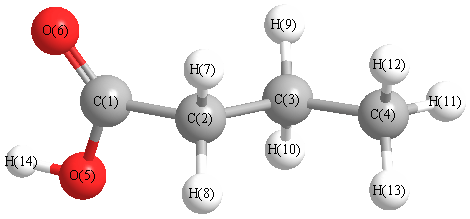Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3812 |
3648 |
60.08 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3150 |
3015 |
26.96 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3142 |
3007 |
23.14 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3135 |
3000 |
18.48 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3107 |
2974 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3072 |
2940 |
22.64 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3060 |
2928 |
5.14 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3054 |
2922 |
19.99 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1877 |
1797 |
302.09 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1504 |
1439 |
5.81 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1494 |
1430 |
7.67 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1489 |
1425 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1467 |
1404 |
8.02 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1409 |
1349 |
7.19 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1400 |
1340 |
65.26 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1379 |
1319 |
6.36 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1324 |
1267 |
1.21 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1287 |
1231 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1259 |
1205 |
31.35 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1217 |
1165 |
129.10 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1122 |
1074 |
7.50 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1087 |
1041 |
49.69 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1070 |
1024 |
14.90 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
937 |
896 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
895 |
857 |
2.54 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
878 |
841 |
5.83 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
757 |
725 |
24.76 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
731 |
699 |
28.04 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
631 |
604 |
68.07 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
581 |
556 |
43.21 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
430 |
412 |
3.20 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
333 |
318 |
0.87 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
248 |
238 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
187 |
179 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
97 |
93 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
37 |
35 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26328.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.957) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25196.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.426 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.332 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.241 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.450 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.394 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.360 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.157 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.155 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.140 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.149 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.316 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.167 |
1.303 |
0.313 |
1.777 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-35.831 |
5.326 |
0.418 |
| y |
5.326 |
-37.905 |
-1.309 |
| z |
0.418 |
-1.309 |
-35.507 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.875 |
5.326 |
0.418 |
| y |
5.326 |
-2.236 |
-1.309 |
| z |
0.418 |
-1.309 |
1.361 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.722 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.074 |
|---|
| xy | 5.326 |
|---|
| xz | 0.418 |
|---|
| yz | -1.309 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.861 |
-0.036 |
-0.269 |
| y |
-0.036 |
7.171 |
0.052 |
| z |
-0.269 |
0.052 |
6.109 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
207.068 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.390 |