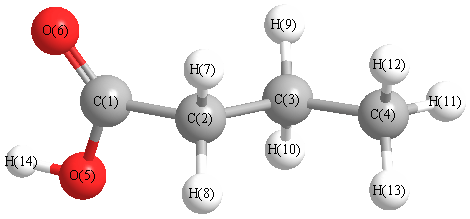Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3766 |
3621 |
68.10 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3150 |
3028 |
31.20 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3146 |
3025 |
21.77 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3137 |
3016 |
16.41 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3111 |
2991 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3068 |
2950 |
28.03 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3058 |
2940 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3053 |
2935 |
25.45 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1877 |
1805 |
325.63 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1481 |
1424 |
6.78 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1469 |
1413 |
8.61 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1467 |
1410 |
1.40 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1443 |
1387 |
10.76 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1407 |
1353 |
66.25 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1397 |
1343 |
13.57 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1374 |
1321 |
8.25 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1318 |
1267 |
2.21 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1277 |
1228 |
3.01 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1253 |
1205 |
49.28 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1217 |
1170 |
120.36 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1125 |
1082 |
6.95 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1093 |
1051 |
29.79 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1077 |
1035 |
20.19 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
942 |
906 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
893 |
858 |
3.39 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
876 |
842 |
5.51 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
760 |
730 |
19.75 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
721 |
693 |
42.63 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
628 |
604 |
67.95 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
576 |
554 |
39.93 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
436 |
420 |
3.14 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
336 |
323 |
0.97 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
257 |
247 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
189 |
182 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
96 |
92 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
38 |
36 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26253.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9615) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25242.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.039 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.121 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.079 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.184 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.256 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.057 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.068 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.055 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.045 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.047 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.044 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.158 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.160 |
1.272 |
0.328 |
1.752 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.492 |
5.476 |
0.567 |
| y |
5.476 |
-38.080 |
-1.154 |
| z |
0.567 |
-1.154 |
-35.865 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.480 |
5.476 |
0.567 |
| y |
5.476 |
-1.902 |
-1.154 |
| z |
0.567 |
-1.154 |
1.421 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.843 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.588 |
|---|
| xy | 5.476 |
|---|
| xz | 0.567 |
|---|
| yz | -1.154 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.849 |
-0.037 |
-0.284 |
| y |
-0.037 |
7.199 |
0.034 |
| z |
-0.284 |
0.034 |
5.979 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
208.353 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.434 |