Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3778 |
3618 |
35.82 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3635 |
3482 |
36.26 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3136 |
3003 |
30.68 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3133 |
3001 |
45.33 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3109 |
2978 |
1.57 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3079 |
2949 |
13.50 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3071 |
2941 |
18.68 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3047 |
2918 |
26.65 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3036 |
2907 |
14.08 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1826 |
1749 |
264.67 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1611 |
1543 |
121.82 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1502 |
1438 |
4.45 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1494 |
1430 |
6.10 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1482 |
1420 |
3.45 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1455 |
1393 |
5.32 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1415 |
1355 |
86.39 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1404 |
1344 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1356 |
1298 |
35.70 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1317 |
1261 |
8.95 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1252 |
1199 |
44.83 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1241 |
1188 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1139 |
1090 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1107 |
1060 |
1.39 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1084 |
1038 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1059 |
1014 |
2.03 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
936 |
896 |
1.99 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
881 |
844 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
844 |
808 |
2.94 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
743 |
712 |
6.72 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
650 |
623 |
4.24 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
613 |
587 |
13.00 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
511 |
489 |
3.61 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
420 |
402 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
340 |
325 |
3.17 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
248 |
237 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
180 |
172 |
9.00 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
150 |
144 |
183.37 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
96 |
92 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
26 |
25 |
2.36 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28701.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9577) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27487.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
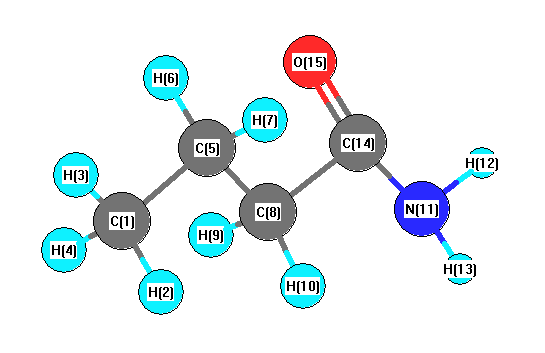
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.410 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.120 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.187 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.138 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.330 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.117 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.135 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.565 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.271 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.268 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.442 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.371 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.417 |
-3.401 |
0.033 |
3.427 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.072 |
-5.877 |
0.012 |
| y |
-5.877 |
-38.072 |
-0.220 |
| z |
0.012 |
-0.220 |
-37.095 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.512 |
-5.877 |
0.012 |
| y |
-5.877 |
-3.489 |
-0.220 |
| z |
0.012 |
-0.220 |
-2.023 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.046 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.000 |
|---|
| xy | -5.877 |
|---|
| xz | 0.012 |
|---|
| yz | -0.220 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.582 |
-0.331 |
-0.103 |
| y |
-0.331 |
8.108 |
0.034 |
| z |
-0.103 |
0.034 |
6.090 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
215.255 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.672 |