Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3599 |
3446 |
17.08 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3222 |
3086 |
13.25 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3197 |
3062 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3179 |
3044 |
17.72 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1677 |
1606 |
127.61 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1646 |
1576 |
25.13 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1539 |
1474 |
60.98 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1323 |
1267 |
45.41 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1196 |
1145 |
7.48 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1057 |
1012 |
2.08 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1002 |
959 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
978 |
937 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
889 |
852 |
9.51 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
834 |
799 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
773 |
740 |
55.08 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
711 |
681 |
13.74 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
603 |
577 |
261.78 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
525 |
503 |
0.87 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
506 |
485 |
63.88 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
223 |
213 |
4.66 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3704 |
3547 |
13.64 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3202 |
3066 |
35.01 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
3180 |
3046 |
3.85 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1649 |
1579 |
4.55 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1503 |
1440 |
2.35 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1377 |
1319 |
8.80 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1349 |
1292 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1172 |
1122 |
1.11 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1135 |
1087 |
3.84 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1069 |
1024 |
2.33 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
950 |
910 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
837 |
802 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
618 |
592 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
413 |
395 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
373 |
358 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
303 |
290 |
17.66 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25755.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9577) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24666.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
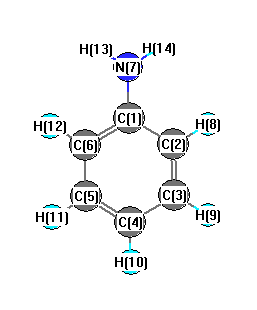
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.355 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.198 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.093 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.152 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.093 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.198 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.627 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.101 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.257 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.257 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.999 |
1.320 |
0.000 |
1.656 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-44.757 |
-3.123 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.123 |
-33.995 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-36.019 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-9.750 |
-3.123 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.123 |
6.393 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.357 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.714 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.763 |
|---|
| xy | -3.123 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.513 |
-0.110 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.110 |
13.777 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.496 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
190.016 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.785 |