Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3763 |
3613 |
35.62 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3621 |
3476 |
35.29 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3139 |
3014 |
32.47 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3136 |
3011 |
3.24 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3125 |
3000 |
41.08 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3123 |
2998 |
18.65 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3050 |
2928 |
14.76 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3048 |
2926 |
34.60 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3038 |
2916 |
36.41 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1808 |
1736 |
282.89 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1619 |
1555 |
129.96 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1512 |
1452 |
20.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1494 |
1434 |
12.09 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1488 |
1428 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1478 |
1419 |
1.38 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1419 |
1362 |
77.49 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1398 |
1342 |
5.47 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1383 |
1328 |
6.22 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1325 |
1272 |
0.85 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1281 |
1230 |
84.20 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1193 |
1145 |
2.36 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1132 |
1087 |
4.90 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1130 |
1085 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1058 |
1016 |
5.95 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
977 |
938 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
927 |
890 |
3.15 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
923 |
887 |
2.31 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
781 |
750 |
5.38 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
763 |
732 |
4.03 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
613 |
588 |
6.30 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
601 |
577 |
12.99 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
470 |
451 |
3.17 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
319 |
306 |
0.74 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
285 |
274 |
4.10 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
242 |
232 |
6.48 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
241 |
232 |
9.99 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
223 |
214 |
67.93 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
208 |
199 |
111.43 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
21 |
20 |
8.79 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28675.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9601) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27531.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
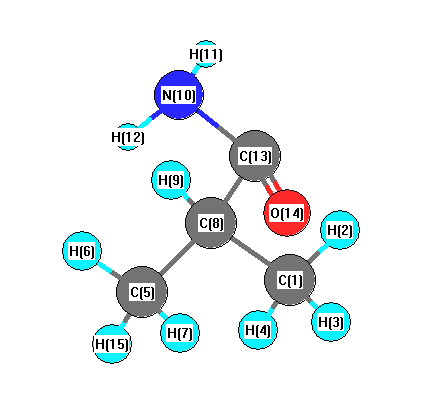
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.306 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.306 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.312 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
N |
-0.469 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.239 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.232 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
C |
0.392 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.375 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.361 |
-0.002 |
-3.578 |
3.596 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.528 |
0.003 |
4.618 |
| y |
0.003 |
-38.168 |
0.000 |
| z |
4.618 |
0.000 |
-38.988 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.050 |
0.003 |
4.618 |
| y |
0.003 |
-2.410 |
0.000 |
| z |
4.618 |
0.000 |
-3.640 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.279 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.640 |
|---|
| xy | 0.003 |
|---|
| xz | 4.618 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.065 |
0.000 |
0.369 |
| y |
0.000 |
7.239 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.369 |
0.000 |
8.095 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
171.137 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.082 |