Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2613.783375 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2613.787010 |
| HF Energy | -2613.783375 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 81.336766 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3195 |
3058 |
5.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1384 |
1325 |
16.12 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
733 |
701 |
17.75 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
144 |
137 |
68.80 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
3353 |
3209 |
0.49 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
931 |
891 |
1.13 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4869.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9571) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4660.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
1.473 |
0.000 |
| Br2 |
0.000 |
-0.365 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-0.000 |
1.973 |
0.950 |
| H4 |
-0.000 |
1.973 |
-0.950 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| C1 | | 1.8377 | 1.0739 | 1.0739 |
Br2 | 1.8377 | | 2.5242 | 2.5242 | H3 | 1.0739 | 2.5242 | | 1.8999 | H4 | 1.0739 | 2.5242 | 1.8999 | |
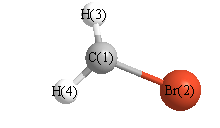 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
117.802 |
|
Br2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.802 |
| H3 |
C1 |
H4 |
124.396 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.301 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.934 |
0.000 |
0.934 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.202 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
-21.890 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.245 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.134 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
3.333 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.199 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.399 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.311 |
|---|
| xy | -0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.079 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
6.124 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.538 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
42.332 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.506 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2613.783366 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -2613.783366 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 81.362975 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3193 |
3056 |
5.05 |
119.06 |
0.11 |
0.19 |
| 2 |
A1 |
1384 |
1325 |
16.02 |
0.84 |
0.66 |
0.80 |
| 3 |
A1 |
729 |
698 |
17.75 |
9.83 |
0.18 |
0.31 |
| 4 |
B1 |
140 |
134 |
68.78 |
0.07 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B2 |
3351 |
3207 |
0.49 |
55.99 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
931 |
891 |
1.14 |
2.26 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4863.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9571) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4655.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.472 |
| Br2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.365 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.950 |
-1.973 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-0.950 |
-1.973 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| C1 | | 1.8370 | 1.0739 | 1.0739 |
Br2 | 1.8370 | | 2.5237 | 2.5237 | H3 | 1.0739 | 2.5237 | | 1.8996 | H4 | 1.0739 | 2.5237 | 1.8996 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
117.820 |
|
Br2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.820 |
| H3 |
C1 |
H4 |
124.359 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.302 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.151 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.932 |
0.932 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.200 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-24.245 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.893 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.131 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.199 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.329 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.659 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.955 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.079 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.537 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.122 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
42.315 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.505 |
