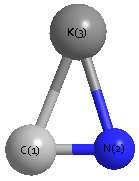Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.506507 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.505793 |
| HF Energy | -692.362527 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 61.054993 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.305 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.274 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.449 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.5786 | 3.7538 |
C2 | 2.5786 | | 1.1753 | N3 | 3.7538 | 1.1753 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.639 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.446 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.193 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.870 |
11.870 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.050 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.050 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.009 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.480 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.480 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-6.959 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -13.919 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.452 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.452 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.354 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
99.913 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.996 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.509029 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -692.367972 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.657800 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.204 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.396 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.214 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.6004 | 2.4175 |
C2 | 3.6004 | | 1.1829 | N3 | 2.4175 | 1.1829 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.677 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.368 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.309 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.776 |
11.776 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.043 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.043 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-32.373 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.665 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.665 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.330 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -18.661 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.389 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.389 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.096 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
88.642 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.415 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.516130 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.516043 |
| HF Energy | -692.373029 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 68.888696 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.033 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.634 |
-1.580 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.543 |
-1.450 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.6888 | 2.5424 |
C2 | 2.6888 | | 1.1841 | N3 | 2.5424 | 1.1841 | |
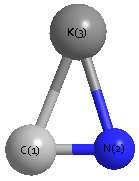 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
70.095 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
83.935 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.970 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.598 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.321 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.277 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.482 |
9.710 |
0.000 |
9.722 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.386 |
0.831 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.831 |
-25.533 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.330 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.954 |
0.831 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.831 |
-0.175 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.130 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.259 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.852 |
|---|
| xy | 0.831 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.468 |
-0.118 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.118 |
4.550 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.527 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
70.336 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.387 |